Traffic dramatically underestimated as major nitrogen oxide polluter
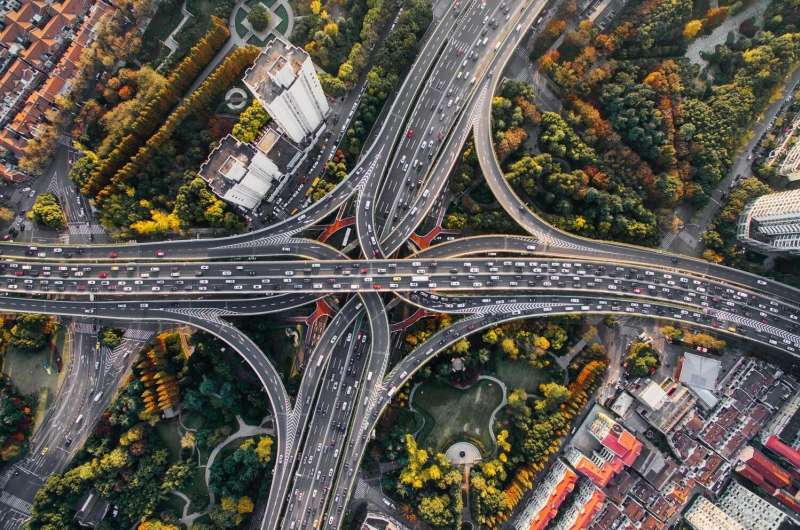

Traffic contributes more to nitrogen oxide emissions in Europe than previously thought. This is the result of a current study carried out by scientists from the University of Innsbruck. The research team headed by Thomas Karl shows that even newer air quality models underestimate traffic related nitrogen oxide pollution by up to a factor of 4. The results of the study are published in the Nature journal Scientific Reports.
In metropolitan areas throughout Europe maximum permissible values of nitrogen oxide are consistently breached. It has been a challenge to determine how much each polluter contributes to the emission output. Until now emission levels were mainly calculated by collecting emission data at laboratory testing facilities and subsequently extrapolating them in models. However, the amount of pollutant emissions that vehicles emit on a daily basis depends on numerous factors, for example on individual driving behavior. The recent Diesel scandal showed, for example, that measurements at engine test stands based on the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) or similar emission testing procedures can be highly uncertain for predicting actual environmental impacts. A large number of new studies have recently been published suggesting that emission levels from test stands have to be adjusted upwards.
Environmental protection and health agencies base their air pollution management on atmospheric models that rely on these experimental data from test facilities. While there have been some doubts about nitrogen oxide emissions for some time, scientists lacked the technology to measure the actual amount of emitted pollutants in a specific area and to determine their overall source strength. A team of physicists headed by Thomas Karl from the Institute of Atmospheric and Cryospheric Sciences at the University of Innsbruck has now implemented a process to do exactly that in the center of Innsbruck, Austria.
Actual nitrogen oxide emissions up to four times higher
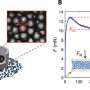
The researchers from Innsbruck use a special measurement method – the so-called eddy-covariance method – to continuously monitor the concentration of trace gases in air, which enables them to determine the emissions in an urban area. "We continuously measure the concentration of carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide and volatile organic compounds at our urban observatory in Innsbruck. We record 36,000 data points per hour," explains Karl. Using statistical methods, the scientists infer emissions from these data within a radius of about one kilometer of the measurement location. The analysis of the data of a three months long measurement campaign, which took place in 2015 and is now published in Scientific Reports, shows two main sources for nitrogen oxide concentrations in the Innsbruck air: traffic and residential combustion, with traffic accounting for more than 80 % of the nitrogen oxide emissions in the surroundings of the test station at the University. The majority of the emissions is caused by Diesel cars. "This result is relatively representative for the whole city," says Karl who points out the far-reaching relevance of the results: "Even newer atmospheric models are based on emission inventories that underestimate nitrogen oxide emission levels up to a factor of four." The actual nitrogen oxide emission levels may be four times higher than predicted in the some models.
Tracking down the main polluter
Nitrogen oxide is toxic in higher concentrations and classified as hazardous air pollutant. In addition, it contributes to the development of ground-level ozone. Regulatory thresholds are meant to limit emissions. However, in Innsbruck, for example, the average level of nitrogen oxide is 36 times higher than the new emission regulation standard laid out in the Clean Air Act in the USA. Because of the high levels of nitrogen oxide along the motorways of the Inn valley and the Brenner pass, driving bans and speed limits pursuant to the Austrian Clean Air Protection Act (IG-L) have already been introduced. The aim of the current study is to determine the main polluters of nitrogen oxide emissions in more detail. The Tyrolean scientists' future goal is to use their setup to investigate the impact of the motorway in the Lower Inn valley, extend their measurements in Innsbruck to the winter months and study the impact of agricultural activities. Moreover, air researcher Karl wants to establish longer measurement series'. An important step towards this goal is the establishment of the Innsbruck Atmospheric Observatory (IAO), which is currently being built at the Campus Innrain. It will be used by various research groups at the University of Innsbruck.
More information: T. Karl et al. Urban eddy covariance measurements reveal significant missing NOx emissions in Central Europe, Scientific Reports (2017). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02699-9
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by University of Innsbruck