Biologists increased the proportion of medicinal substances in plants
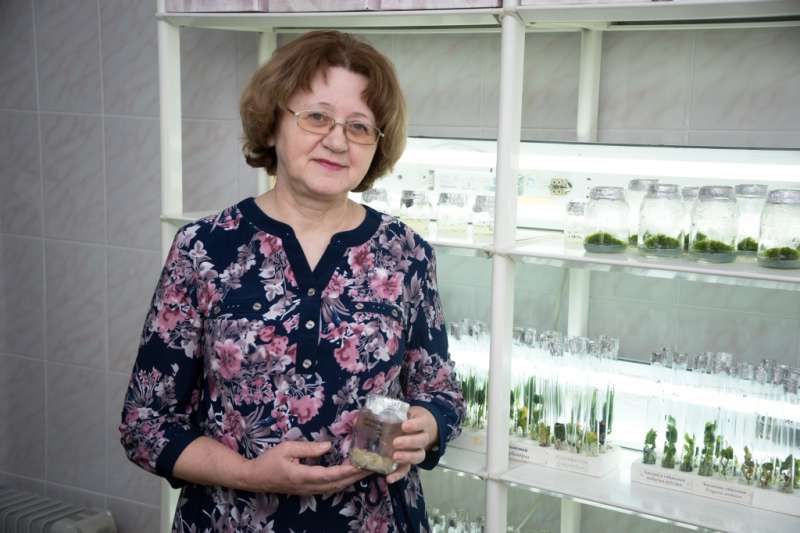

Tomsk State University biologists have developed a technology for obtaining cell cultures with a high content of a number of biologically active substances (BAS). It is important for pharmaceuticals, and will also help to conserve endangered species of medicinal plants.
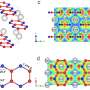
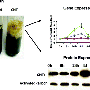
The Department of Plant Physiology and Biotechnology has already obtained cell cultures and microclones of medicinal plants containing substances with anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, nootropic, and sedative effects: flavonoids, saponins, furanocoumarins, ecdysteroids, and others. It also selected variants of nutrient media, thanks to which the amount of BAS has increased.
"Not all herbal medicinal substances have synthetic analogs, and the use of plants from natural populations causes severe damage to the latter and requires high costs. Therefore, currently many BASs are being obtained by a special process of growing cell cultures," says Irina Golovatskaya, professor at the Department of Plant Physiology and Biotechnology.
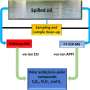
The essence of the process is that the pieces of plant tissue are sterilized and placed in an artificial environment where cells actively divide, forming a callus. Then the pieces of callus are transferred to different nutrient media, which include micro- and macro-elements, cell division hormones, and sucrose.
"By changing the hormonal balance and the chemical composition of the medium and introducing additional substances we can achieve an increase in the number of secondary metabolites in the cells (BAS). They are not obligatory for the plant organism, but they arise as a protective reaction to unfavorable environmental conditions - temperature changes, plant pests, and others. At the same time, their share is often higher than in wildlife," explains Irina Golovatskaya.
There are other advantages: Cell cultures can be cultivated year round, regardless of weather conditions. Moreover, it's ecologically clean, while the production of BAS from plant raw material demands removal of unnecessary tissues and pollutants (insects, soils, bacterial and viral substances, and toxics from mushrooms and bacteria).
The next task for scientists is to develop the composition of a nutrient broth in which suspended cell cultures grow more robustly. Then the technology for the production of BAS can be applied industrially.
Provided by Tomsk State University