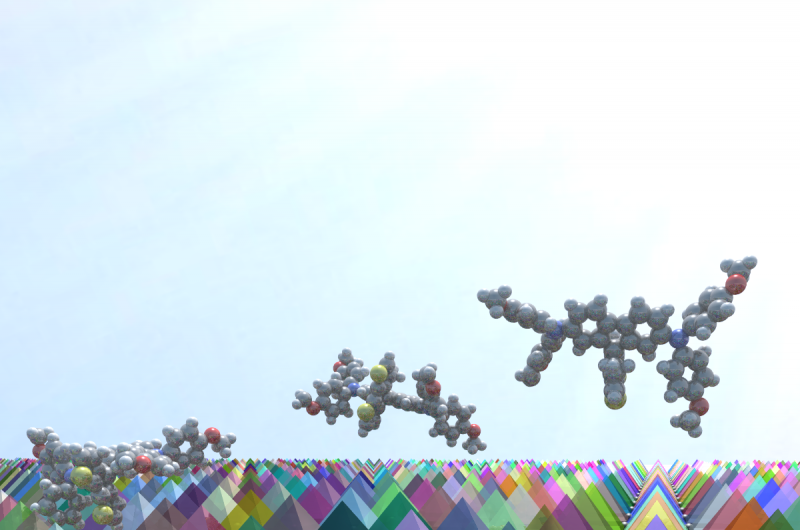
3-D illustration of FDT molecules on a surface of perovskite crystals. Credit: Credit: Sven M. HeinCopyright: EPFL
EPFL scientists have developed a solar-panel material that can cut down on photovoltaic costs while achieving competitive power-conversion efficiency of 20.2%.
Some of the most promising solar cells today use light-harvesting films made from perovskites - a group of materials that share a characteristic molecular structure. However, perovskite-based solar cells use expensive "hole-transporting" materials, whose function is to move the positive charges that are generated when light hits the perovskite film. Publishing in Nature Energy, EPFL scientists have now engineered a considerably cheaper hole-transporting material that costs only a fifth of existing ones while keeping the efficiency of the solar cell above 20%.
As the quality of perovskite films increases, researchers are seeking other ways of improving the overall performance of solar cells. Inadvertently, this search targets the other key element of a solar panel, the hole-transporting layer, and specifically, the materials that make them up. There are currently only two hole-transporting materials available for perovskite-based solar cells. Both types are quite costly to synthesize, adding to the overall expense of the solar cell.
To address this problem, a team of researchers led by Mohammad Nazeeruddin at EPFL developed a molecularly engineered hole-transporting material, called FDT, that can bring costs down while keeping efficiency up to competitive levels. Tests showed that the efficiency of FDT rose to 20.2% - higher than the other two, more expensive alternatives. And because FDT can be easily modified, it acts as a blueprint for an entire generation of new low-cost hole-transporting materials.
"The best performing perovskite solar cells use hole transporting materials, which are difficult to make and purify, and are prohibitively expensive, costing over €300 per gram preventing market penetration," says Nazeeruddin. "By comparison, FDT is easy to synthesize and purify, and its cost is estimated to be a fifth of that for existing materials - while matching, and even surpassing their performance."
More information: Saliba M, Orlandi S, Matsui T, Aghazada S, Cavazzini M, Correa-Baena J-P, Gao P, Scopelliti R, Mosconi E, Dahmen KH, De Angelis F, Abate A, Hagfeldt A, Pozzi G, Graetzel M, Nazeeruddin MK. A molecularly engineered hole-transporting material for e cient perovskite solar cells. Nature Energy 15017, 18 January 2016. DOI: 10.1038/NENERGY.2015.17
Journal information: Nature Energy
Provided by Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne