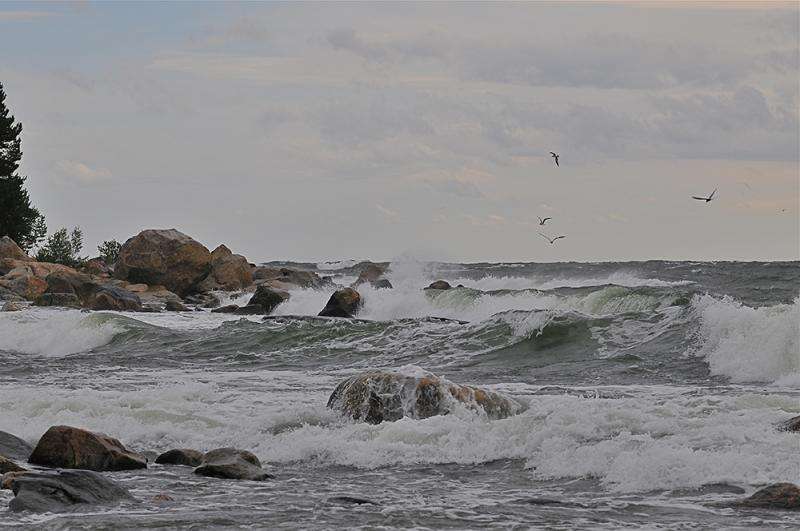
Ocean with rocks. Credit: Mostphotos
By examining rocks at the bottom of ancient oceans, an international group of researchers have revealed that arsenic concentrations in the oceans have varied greatly over time. But also that in the very early oceans, arsenic co-varied with the rise of atmospheric oxygen and coincided with the coming and going of global glaciations. The study was recently published in the Nature Group Journal, Scientific Reports.
"In the article we argue that when we first see the appearance of complex life on Earth, is when life have developed mechanisms to resist catastrophic chemical changes forced by global glaciations. And that this enabled the expansion of complex life in oceans, and paved the way for our own evolution", says Dr Ernest Chi Fru of Stockholm University, who has led the research group.
The first appearance of oxygen in the atmosphere occurred at a time when marine arsenic concentrations were dramatically low, at about after 2.45 billion years ago. This is also a period when Earth experienced its first known global glaciation. At the end of these glaciations, considerable rise in marine arsenic concentrations concurred with rapid demise of atmospheric oxygen.
The authors infer—from the way modern photosynthetic organisms react to changing marine arsenic concentrations—that this event was due to widespread ocean toxicity resulting from the release of toxic elements into the oceans when the ice melted.
A similar low and high arsenic content accompanied the coming and going of global glaciations at around 0.7 billion years ago, which is when Earth first saw the appearance of complex life. While the low marine arsenic concentrations again coincide with a rapid rise in atmospheric oxygen content to near modern day levels at this time, the subsequent increase when the ice melted is not accompanied by atmospheric oxygen decline.
More information: Arsenic Stress after the Proterozoic Glaciations, Scientific Reports, 2015.
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Stockholm University