Cells starved of oxygen and nutrients condense their DNA
Scientists at the Institute of Molecular Biology (IMB) have been able to see, for the first time, the dramatic changes that occur in the DNA of cells that are starved of oxygen and nutrients. This starved state is typical in some of today's most common diseases, particularly heart attacks, stroke and cancer. The findings provide new insight into the damage these diseases cause and may help researchers to discover new ways of treating them.
When a person has a heart attack or stroke, the blood supply to part of their heart or brain is blocked. This deprives affected cells there of oxygen and nutrients (a condition known as ischaemia) and can cause long-term damage, meaning that the person may never fully recover. Ina Kirmes, a PhD student in the group of Dr. George Reid at IMB, investigated what happens to the DNA in cells that are cut off from their oxygen and nutrient supply.
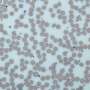
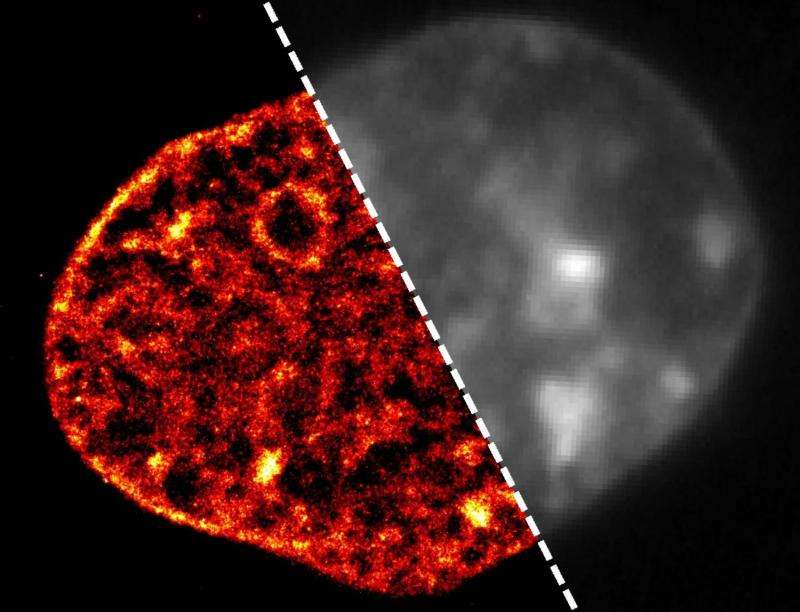
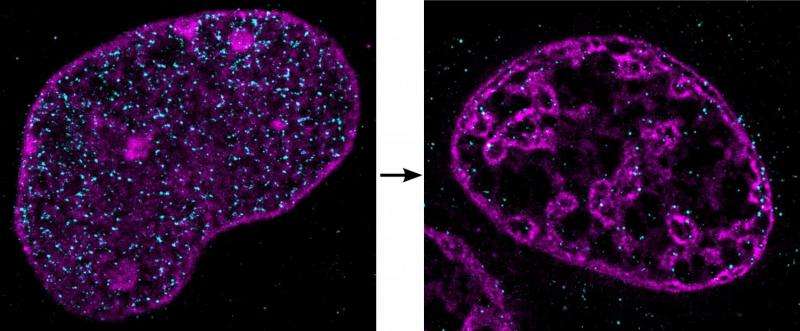
In a healthy cell, large parts of the DNA are open and accessible. This means that genes can be easily read and translated into proteins, so that the cell can function normally. However, the researchers showed that, in ischaemia, DNA changes dramatically: it compacts into tight clusters. The genes in this clumped DNA cannot be read as easily anymore by the cell, their activity is substantially reduced and the cell effectively shuts down. If cells in a person's heart stop working properly, this part of the heart stops beating, and they will have a heart attack. Similarly, when blood supply is blocked to cells in someone's brain and their cells there are starved of oxygen and nutrients, they have a stroke.
Dr. Reid is excited about the implications of this finding. "When you have a stroke, when you have a heart attack, this is likely to be what's happening to your DNA", he explains. "Now we know that this is what's going on, we can start to look at ways of preventing this compaction of DNA."
The key to this discovery was a close collaboration with Aleksander Szczurek, joint first author on this publication, who is part of the group of Prof. Christoph Cremer at IMB. They developed a new method that made it possible to see DNA inside the cell at a level of detail never achieved before. Their technique is a further development of "super-resolution light microscopy", which uses blinking dyes that bind to DNA to enable the researchers to define the location of individual molecules in cells. This novel technology has been described in a separate paper, published in Experimental Cell Research in September 2015.
More information: I. Kirmes et al. (2015), A transient ischemic environment induces reversible compaction of chromatin, Genome Biology 16:246, DOI: 10.1186/s13059-015-0802-2
D. Żurek-Biesiada et al. (2015), Localization microscopy of DNA in situ using Vybrant® DyeCycle™ Violet fluorescent probe: A new approach to study nuclear nanostructure at single molecule Resolution, Experimental Cell Research, DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.08.020
Journal information: Genome Biology
Provided by Universitaet Mainz