New research could revolutionize farming in developing world
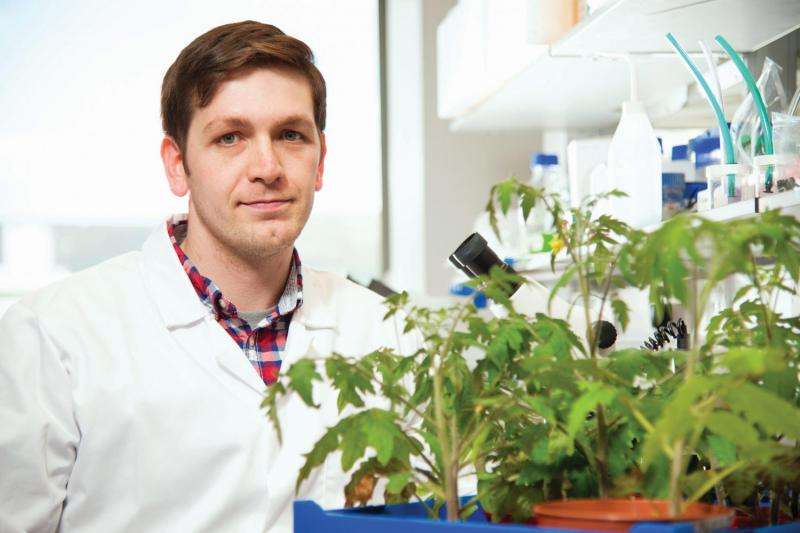

A brand new technology developed by researchers at Queen's University Belfast, Northern Ireland, has the potential to reduce crop losses across the developing world and boost the incomes of subsistence farmers.
The technology is designed to combat parasitic 'nematodes' - microscopic worms which infect crop plants from the soil, and are responsible for a 12.3% reduction in global agricultural productivity, a loss of around £100 billion annually.
The research, which involves using 'peptide mimics' - versions of the parasites' own brain chemistry - to confuse the real parasites and ultimately, render them impotent, has been awarded a Phase II Grand Challenges Exploration grant of $1million from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to be developed in Belfast and proceed to trials in Kenya.
The project will focus on banana and plantain - although in theory it could extend to other crops - which are cultivated across 130 countries, making them the eighth most produced staple in the world. The fruits are often grown by smallholders in the developing world and can account for up to 30 per cent of farmers' income. Despite their popularity, however, the crop is highly susceptible to a variety of plant parasitic nematodes, which typically reduce yields by 30-50 per cent.
Lead researcher on the project, Dr Johnathan Dalzell from Queen's Institute for Global Food Security said: "This project builds on our previous research where we developed a novel way of interfering with parasitic nematode host-finding behaviour. Through our lab work we have identified a family of peptide mimics, which specifically and potently interfere with their neurobiology, disorientating the parasites so they can't find the host plant. They then die quickly through lack of food. Importantly, these peptide mimics appear to have no impact on non-target animals. This is a clean, and robust approach to parasite control.
"Our aim is to develop a variety of approaches which harness this new technology in order to protect crops plants from these parasitic worms. We have chosen to focus on banana and plantain as these crops are highly susceptible to a range of pests and diseases, including nematodes, insects, viral and fungal pathogens. Developing a broad-spectrum nematode control strategy represents a significant challenge, especially in sub-Saharan Africa, which is a hotbed for pathogens which can break resistance strategies. This is yet another example of how Queen's is having a global impact and is using its research findings to improve how our world functions."
As a result of the Gates Foundation grant and other funding, the Queen's-led project will proceed to glasshouse trials, in association with the International Institute for Tropical Agriculture in Nairobi, Kenya. Subsequently, field trials will be conducted and regulatory approval sought.
Provided by Queen's University Belfast