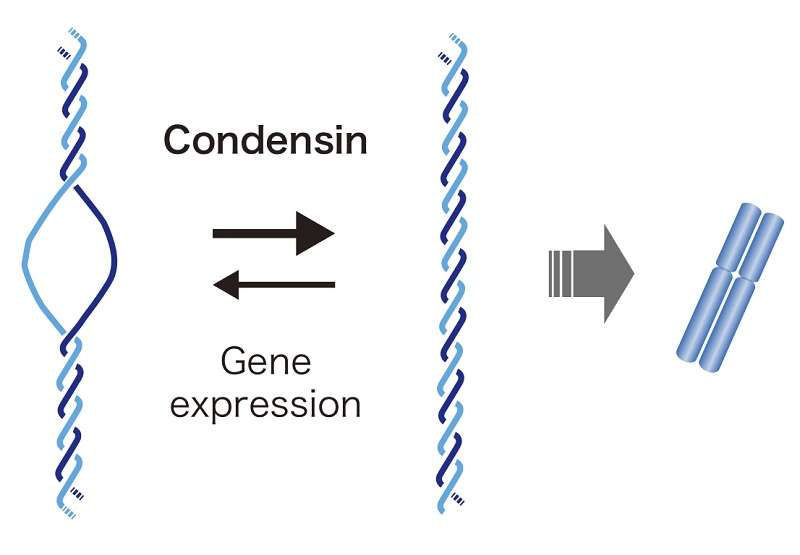
Condensin recognizes unwound DNA segments produced by gene expression and restores them to double-stranded DNA. This function proved to be a prerequisite for making chromosomes from DNA. Credit: Takashi Sutani
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have discovered a long-overlooked process important for converting a long, string-like DNA molecule into a chromosome. This finding gives us a better understanding of the mechanism of how cells store safely genetic material, DNA.
DNA molecules are long, string-like polymers storing the genetic information of life and, in a cell, are tightly packed into structures called chromosomes. Formation of chromosomes in a dividing cell is required for faithful transmission of information in DNA to daughter cells. The condensin complex is known to play an essential role in assembling chromosomes, but it remains unknown how condensin is involved in folding of DNA molecules.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo, including Assistant Professor Takashi Sutani, Professor Katsuhiko Shirahige (Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biosciences) and Ph.D student Toyonori Sakata (Graduate School of Agricultural and Life Sciences), isolated from cells and analyzed DNA segments to which condensin binds, and revealed that condensin is associated with single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) which is produced by unwinding of the DNA double-helix.
By measuring the amount of ssDNA using an ssDNA binding protein, they found that ssDNA regions existed at expressed genes and were produced by gene expression (or transcription), and that ssDNA amount was further increased in condensin-deficient cells. They also discovered that chromosome segregation defects in mutant cells that showed lowered levels of condensin function were largely rescued by transcription inhibition. They therefore concluded that ssDNA is produced by unwinding of double-stranded DNA during transcription, that ssDNA is detrimental to assembling chromosomes, and that condensin restores unwound ssDNA segments to double-stranded DNA.
"It was widely believed that unwound DNA segments return spontaneously to canonical double-helical DNA, but this study has revealed that restoration of double-stranded DNA is actively regulated and is important for cell survival. It has also demonstrated for the first time that the presence of ssDNA impedes chromosome organization, providing insight into the mechanism of chromosome formation," says Assistant Professor Sutani.
More information: "Condensin targets and reduces unwound DNA structure associated with transcription in mitotic chromosome condensation", Nature Communications Online Edition: 2015/7/23 (Japan time), DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8815
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by University of Tokyo