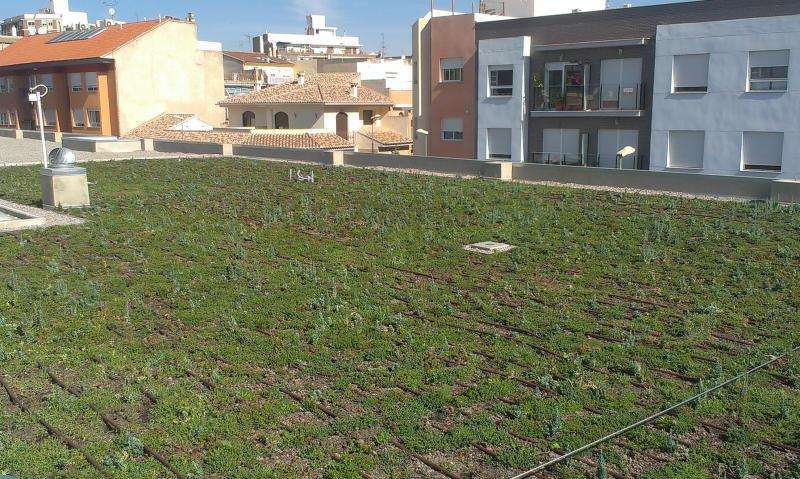
Green roof in the town of Benaguasil
A decision support tool is one of the latest developments for the management and use of stormwater and the improvement of energy efficiency in the urban water cycle. The software has been developed within the EU-MED Programme project E²STORMED, led by the Universitat Politècnica de València, and applied in six Mediterranean cities.
Water and wastewater facilities frequently represent the largest and most energy-intensive loads owned and operated by water utilities, representing up to 35% of municipal energy use. "Therefore," says Ignacio Escuder, professor at the Institute of Engineering of Water and Environment of the Universitat Politècnica de València, "it is expected that improvements in energy efficiency in managing urban water cycle will translate into a significant reduction of energy consumption. In addition, recent data suggest that energy efficiency can reduce up to 60% of C02 emissions linked to this activity."
Also, urban development usually increases the impervious surface, soils are compacted and infiltration processes are reduced. These changes increase the peak flow and volume of runoff, which causes in unitary systems large volumes of water reaching wastewater treatment plants where in many cases it cannot be treated.
The E²STORMED project has analysed the impact on energy efficiency of the use of innovative stormwater solutions over the past two years, such as Sustainable drainage systems (SuDS), which represent a flexible and economically efficient urban drainage that can help improve comfort in the cities and reduce spending on energy consumption.
The researchers explain the SuDS make use of common sense and simple technologies such as beds of native plants, rain barrels, green roofs and porous surfaces for car parking and roads. In addition to reducing potable water use, the result is less water pollution from contaminated runoff, less flooding, replenished water supplies, and often more natural-looking, aesthetically pleasing cityscapes.
The project, which ended this month, promotes the implementation of these systems in Mediterranean cities, where their use is not widespread unlike the Anglo-Saxon and Nordic countries. The Energy Engineering Institute of the Universitat Politècnica de València also took part in the project together with eight other partners from Spain, Italy, UK, Croatia, Montenegro, Greece and Malta.
E²STORMED decision support tool
As part of the project, E²STORMED has developed a decision support tool to include energy efficiency and environmental criteria in urban stormwater management decisions. The tool has been developed using the pilot cities to compare and evaluate different scenarios of combining conventional and sustainable drainage systems. "The results of applying this tool will allow more sustainable, informed and objective stormwater management," says Ignacio Escuder. This tool can be downloaded free at: www.e2stormed.eu
The decision support tool developed within E²STORMED quantifies the economic costs, savings, energy consumptions and CO2 emissions of different drainage scenarios in order to include them in a multi-criteria analysis. Thus, decision makers can have complete information presented in a clear and simple way.
The tool has been applied to the management of stormwater in the following Mediterranean cities: Benaguasil (Spain), Pisa (Italy), Hersonissos (Greece), Cetinje (Montenegro), Zagreb (Croatia) and Habbar (Malta). The results and suggestions of these municipalities have improved the tool, ensuring its usefulness for local water management.
Furthermore, within the E²STORMED project a green roof in the town of Benaguasil was built to measure its benefits regarding the management of stormwater and energy efficiency. The first results show that this roof is able to reduce very significantly the peaks and volumes of runoff compared to a conventional one and achieve energy savings of 30% in cooling the building during the hottest days of summer.
Moreover, in each city, local and regional stakeholders were involved in this process through the creation of regional working groups. Thus, it has managed to involve key regional actors relating to the management of water and energy in the transition to a more sustainable and energy efficient management of stormwater.
More information: Improving Energy Efficiency in Urban Stormwater Management in Mediterranean Cities. 13th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Sarawak, Malaysia, 7-12 September 2014
Provided by Asociacion RUVID