Complete camel skeleton unearthed in Austria

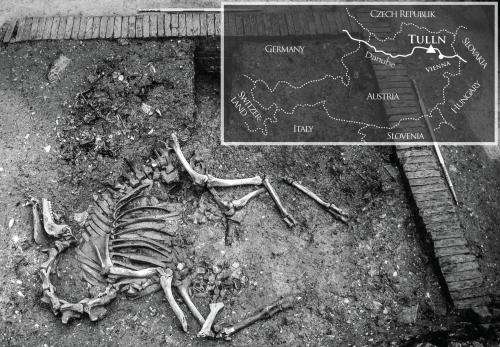
Archaeologists working on a rescue excavation uncovered a complete camel skeleton in Tulln, Lower Austria. The camel, which was dated to the time of the Second Ottoman War in the 17th century, most likely died in the city of Tulln. Genetic analyses showed that the animal was a male hybrid of a dromedary in the maternal line and a Bactrian camel in the paternal line. The find is unique for Central Europe. Archaeozoologists and geneticists from the VetmeduniVienna now published their findings in the journal PLOS ONE.
In 2006 construction began on a new shopping centre in Tulln. The works unearthed various archaeologically valuable objects that were salvaged during rescue excavations. Among these objects was also the complete skeleton of a large mammal.
Large mammal uncovered during excavations in Tulln
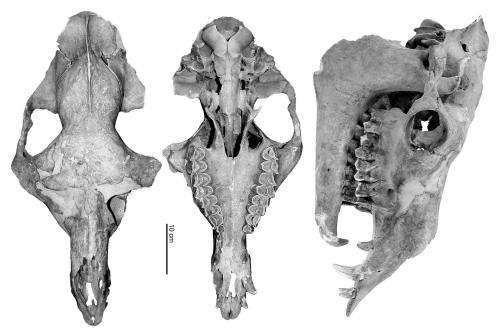
"The partly excavated skeleton was at first suspected to be a large horse or cattle," says archaeozoologist Alfred Galik from the Institute for Anatomy, Histology and Embryology at the University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna. "But one look at the cervical vertebrae, the lower jaw and the metacarpal bones immediately revealed that this was a camel."
Camel bones have been found in Europe dating back to the Roman period. Isolated bones or partly preserved skeletons are known from Mauerbach near Vienna as well as from Serbia and Belgium. But a complete camel skeleton is unique for Central Europe.
"Exotic animal" died in Tulln
In addition to horses, the Ottoman army also used camels for transportation and as riding animals. In cases of scarcity, the soldiers also ate the animal's flesh. But the skeleton found in Tulln was complete. "This means that the animal was not killed and then butchered. It may have been acquired as part of an exchange," says first author Galik. "The animal was certainly exotic for the people of Tulln. They probably didn't know what to feed it or whether one could eat it. Perhaps it died a natural death and was then buried without being used."

Camel was a hybrid
Extensive DNA analysis showed that the animal was a hybrid: its mother was a dromedary and its father a Bactrian camel. The genetic diagnosis confirmed what the scientists saw morphologically. Several of the physical features were that of a dromedary, others of a Bactrian camel. "Such crossbreeding was not unusual at the time. Hybrids were easier to handle, more enduring and larger than their parents. These animals were especially suited for military use," Galik explains.
The camel was male, around seven years old and most likely castrated.
Find dated to the 17th century
Besides animal bones, the excavations also unearthed ceramic plates and other items. A coin - a so-called "Rechenpfenning" - from the time of Louis XIV dates the find to the years between 1643 and 1715. A medicinal bottle containing Theriacum, a medieval remedy from the chemist's shop "Apotheke zur Goldenen Krone" in Vienna was also found at the site. This pharmacy existed between 1628 and 1665, which helped date the site with further precision.
More information: The article "A sunken ship of the desert at the river Danube in Tulln, Austria", by Alfred Galik, Elmira Mohandesan, Gerhard Forstenpointner, Ute Maria Scholz, Emily Ruiz, Martin Krenn and Pamela Burger was published in the scientific journal PLOS ONE.
Journal information: PLoS ONE
Provided by University of Veterinary Medicine—Vienna