Role of gravitational instabilities in volcanic ash deposition: Example of Eyjafjallajokull

Volcanic ash poses a significant hazard for areas close to volcanoes and for aviation. For example, the 2010 eruption of Eyjafjallajökull, Iceland, clearly demonstrated that even small-to-moderate explosive eruptions, in particular if long-lasting, can paralyze entire sectors of societies, with significant, global-level, economic impacts. In this open-access Geology article, Irene Manzella and colleagues present the first quantitative description of the dynamics of gravitational instabilities and particle aggregation based on the 4 May 2010 eruption.
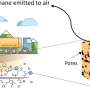
Their analysis also reveals some important shortcomings in the Volcanic Ash Transport and Dispersal Models (VATDMs) typically used to forecast the dispersal of volcanic ash. In particular, specific processes exist that challenge the view of sedimentation of fine particles from volcanic plumes and that are currently poorly understood: particle aggregation and gravitational instabilities. These appear as particle-rich "fingers" descending from the base of volcanic clouds and have commonly been observed during volcanic explosive eruptions.
Based on direct observations of the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull plume, on the correlation with the associated fallout deposit, and on dedicated laboratory analogue experiments, Irene Manzella and colleagues show how fine ash in these particle-rich fingers settles faster than individual particles and that aggregation and gravitational instabilities are closely related. Both phenomena can significantly contribute to reducing fine-ash lifetime in the atmosphere and, therefore, it is crucial to include them in VATDMs in order to provide accurate forecasting of ash dispersal and sedimentation.
More information: The role of gravitational instabilities in deposition of volcanic ash, Irene Manzella et al., Published online ahead of print on 2 Feb. 2015; http://dx.doi.org/10.1130/G36252.1
Journal information: Geology
Provided by Geological Society of America











.jpg)