Scrapie could breach the species barrier

INRA scientists have shown for the first time that the pathogens responsible for scrapie in small ruminants (prions) have the potential to convert the human prion protein from a healthy state to a pathological state. In mice models reproducing the human species barrier, this prion induces a disease similar to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. These primary results published in Nature Communications on 16 December 2014, stress the necessity to reassess the transmission of this disease to humans.
Scrapie is a neurodegenerative disease that has been known for centuries and which affects sheep and goats. Similar to Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) or mad cow disease, scrapie is caused by a transmissible pathogen protein called prion.
However, and contrary to BSE, epidemiological studies have never been able to establish a link between this disease and the occurrence of prion diseases in humans. "Risks of transmitting scrapie to humans (zoonose) were hitherto considered negligible because of the species barrier that naturally prevents prion propagation between species", said Olivier Andreoletti, INRA scientist who led the present study.
Researchers at INRA studied the permeability of the human transmission barrier to pathogens responsible for scrapie, using animal models specifically developed for this purpose. This approach previously allowed the confirmation of the zoonotic nature of prions responsible for BSE in cows and of the variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans (vCJD).
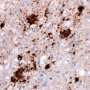
Unexpectedly, in these rodent models, certain pathogens responsible for scrapie were able to cross the transmission barrier. Moreover, the pathogens that propagated through this barrier were undistinguishable from the prions causing the sporadic form of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD). This data suggest a potential link between the occurrence of certain sCJD and these animal prions.
"Since CJD is scarce, about 1 case per million and per year, and incubation periods are usually long -several decades- it is extremely difficult for epidemiological studies to try and make this link", explains Olivier Andreoletti.
In their conclusions, the authors stress the fact that CJD cases are rare though scrapie has been circulating for centuries in small ruminants for which we eat the meat. Even if in future studies scrapie is finally confirmed to have a zoonotic potential, the authors consider that this disease does not constitute a new major risk for public health.
More information: Hervé Cassard, Juan-Maria Torres, Caroline Lacroux, Jean-Yves Douet, Sylvie Benestad, Frédéric Lantier, Séverine Lugan, Isabelle Lantier, Pierrette Costes, Naima Aron, Fabienne Reine, Laetitia Herzog, Juan-Carlos Espinosa, Vincent Beringue and Olivier Andréoletti. "Evidence for zoonotic potential of ovine scrapie prions." Nature Communications, 16 December 2014. DOI: 10.1038/10.1038/NCOMMS6821
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by INRA