Treating pain by blocking the 'chili-pepper receptor'
Biting into a chili pepper causes a burning spiciness that is irresistible to some, but intolerable to others. Scientists exploring the chili pepper's effect are using their findings to develop a new drug candidate for many kinds of pain, which can be caused by inflammation or other problems. They reported their progress on the compound, which is being tested in clinical trials, in ACS' Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
Laykea Tafesse and colleagues explain that decades ago, scientists had pegged a compound called capsaicin as the active ingredient in chili peppers that causes fiery pain. In the 1990s, researchers were able to sequence the genetic sequence for the protein "receptor" that capsaicin attaches to in the body. The receptor is a protein on cells that acts as a gate, allowing only certain substances into a cell. The advance launched a hunt for compounds that can block this gate, cut off the pain signal and potentially treat pain that current drugs are no match for. Some of the molecules resulting from this search have been tested in people but cause unwanted side effects, or they wouldn't work well as oral medication. Tafesse's team wanted to explore variations on this theme to find a better drug candidate.
They produced more than two dozen similar compounds, each with its own unique molecular tweak. They tested them in the lab and in animals for the traits they were looking for, such as potency, safety, the ability to dissolve in water and whether they can be taken orally. One prospect showed the most promise, and it has advanced into clinical trials.
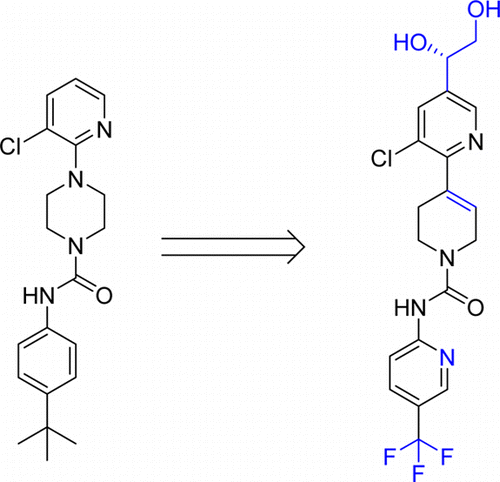
More information: Structure–Activity Relationship Studies and Discovery of a Potent Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid (TRPV1) Antagonist 4-[3-Chloro-5-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-2-pyridyl]-N-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyridine-1-carboxamide (V116517) as a Clinical Candidate for Pain Management, J. Med. Chem., 2014, 57 (15), pp 6781–6794, DOI: 10.1021/jm500818a
Abstract
A series of novel tetrahydropyridinecarboxamide TRPV1 antagonists were prepared and evaluated in an effort to optimize properties of previously described lead compounds from piperazinecarboxamide series. The compounds were evaluated for their ability to block capsaicin and acid-induced calcium influx in CHO cells expressing human TRPV1. The most potent of these TRPV1 antagonists were further characterized in pharmacokinetic, efficacy, and body temperature studies. On the basis of its pharmacokinetic, in vivo efficacy, safety, and toxicological properties, compound 37 was selected for further evaluation in human clinical trials.
Journal information: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Provided by American Chemical Society