Industrial lead pollution beat explorers to the South Pole by 22 years and persists today
Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen became the first man to reach the South Pole in December of 1911. More than 100 years later, an international team of scientists led by Joe McConnell of Nevada's Desert Research Institute (DRI) have proven that air pollution from industrial activities arrived long before.
Using data from 16 ice cores collected from widely spaced locations around the Antarctic continent, including the South Pole, McConnell's team created the most accurate and precise reconstruction to date of lead pollution over the Earth's southernmost continent. The new record, described in an article published today in the online edition of the Nature journal Scientific Reports, spans a 410-year period from 1600 to 2010 A.D.
"Our new record shows the dramatic impact of industrial activities such as smelting, mining, and fossil fuel burning on even the most remote parts of the world," said McConnell, the study's lead author, research professor and director of DRI's ultra-trace ice core analytical laboratory, located on the institute's campus in Reno, Nev.
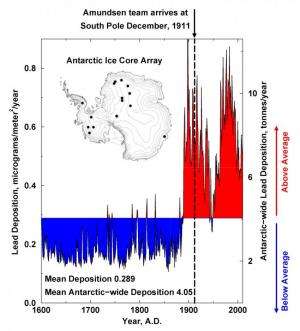
"It is very clear that industrial lead contamination was pervasive throughout Antarctica by the late 19th century, more than two decades before the first explorers made it to the South Pole," he added. "The idea that Amundsen and Scott were traveling over snow that clearly was contaminated by lead from smelting and mining in Australia, and that lead pollution at that time was nearly as high as any time ever since, is surprising to say the least."
All measurements of lead and other chemicals used in this study were made using DRI's unique continuous ice core analytical system. Low background atmospheric concentrations, together with well-known and often distinct isotopic characteristics of industrial sources make lead an ideal tracer of industrial pollution.

"Lead is a toxic heavy metal with strong potential to harm ecosystems," said co-author Paul Vallelonga of the University of Copenhagen. "While concentrations measured in Antarctic ice cores are very low, the records show that atmospheric concentrations and deposition rates increased approximately six-fold in the late 1880's, coincident with the start of mining at Broken Hill in southern Australia and smelting at nearby Port Pirie."
The similar timing and magnitude of changes in lead deposition across Antarctica, as well as the characteristic isotopic signature of Broken Hill lead found throughout the continent, suggest that this single emission source in southern Australia was responsible for the introduction of lead pollution into Antarctica at the end of the 19th century and remains a significant source today, the authors report.
This study included ice cores collected as part of projects funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation. Additional ice cores were contributed to the study by international collaborators including the British Antarctic Survey, the Australian Antarctic Division, and the Alfred Wegener Institute in Germany.
"The ice cores obtained through international collaborations were critical to the success of this study in that they allowed us to develop records from parts of Antarctica not often visited by U.S.-based scientists," said co-author Tom Neumann of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. "This included the Law Dome region of East Antarctica and a big section of East Antarctica visited by the Norwegian-United States Scientific Traverse of East Antarctica."
McConnell explained the hazards of working in such extreme environments. "I remember the day in 1999 we drilled the shallow core about 15 km from South Pole. The temperature was negative 100 degrees Fahrenheit with the wind chill so it was hard to motivate the field team to leave the galley at the South Pole station that day, he said."
Data from the new ice core array illustrates that Antarctic lead concentrations reached a peak in 1900 and remained high until the late 1920's, with brief declines during the Great Depression and the end of World War II. Concentrations then increased rapidly until 1975 and remained elevated until the 1990's.
Concentrations across the Antarctic continent have since declined, but still are about four-fold higher than before industrialization, despite the phase out of leaded gasoline and other mitigation efforts in many countries in the Southern Hemisphere, the report states.
"Our measurements indicate that approximately 660 tonnes (1.5 million pounds) of industrial lead have been deposited on the snow-covered surface of Antarctic during the past 130 years," McConnell said. "While recent contamination levels are lower, clearly detectable industrial contamination of the Antarctic continent persists today… so we still have a ways to go."
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Desert Research Institute