Flexible pressure-sensor film shows how much force a surface 'feels'—in color
Imagine an automobile crash test that uses test dummies painted all over with a substance that can change color according to the levels of stress that various parts of the dummies' bodies will endure. Such a "color map" could provide vital information to engineers designing safer automobiles.
Or imagine baseball gloves that when worn show the batters if they are using the appropriate amount of pressure to grip their bats, resulting in better performance.
New technology developed at the University of California, Riverside may now make the above and similar ideas a reality. Indeed, the technology could be applied to improve everyday devices, such as smartphones, that for operation rely on the right amount of pressure applied to them.
"We have developed a high-resolution pressure sensor that indicates pressure by varying its color—a sensor that all of us can use with just our eyes," said Yadong Yin, an associate professor of chemistry, whose lab led the research.
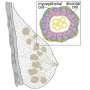
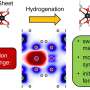
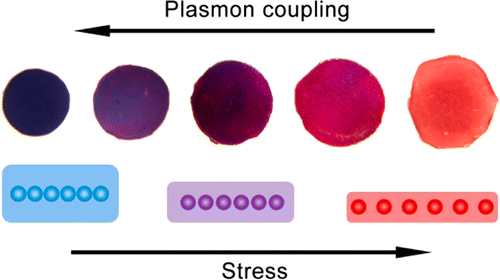
The lab used a self-assembly method to string together gold nanoparticles which they then embedded into a polymer film. The film deformed when pressed, stretching the gold nanoparticle strings by increasing the separation between neighboring gold nanoparticles.
"This increased separation alters the way the nanoparticles interact with light," Yin explained. "When linked together, the gold nanoparticles originally appear blue. But they gradually change to red with increasing pressure as the nanoparticles start disassembling. This easily and visually helps us figure out how much pressure has been applied."
Study results appear this month in Nano Letters.
The sensor that Yin's lab developed differs from commercially available pressure sensor films. The latter indicate pressure by changing the intensity of just one color (for example, a pale red to a darker red). They tend to be difficult to interpret and have low resolution and contrast.
The new technology produces a mosaic of easy-to-distinguish colors and has the benefit of higher contrast and resolution. It can potentially be used in many safety devices for revealing pressure distribution over even very complex surfaces.
"The many electronic stress sensors commercially available are bulky and not suitable for certain applications," Yin said. "For example, it is difficult to tell the stress distribution over a particular area if the contact surfaces are not flat and uniform. Our sensor films can be painted on the contact surfaces so that the color variance in different areas clearly shows the stress distribution over the contact surface."
While his lab used gold in the experiments, silver and copper could also work, Yin added. The sensor the lab developed is a solid plastic film. Under stress, it deforms like conventional plastics. The new color that arises persists after the stress is removed.
"This is why we are calling it a 'colorimetric stress memory sensor,'" Yin said.
One of the research interests of his lab is the design of materials with new properties via the self-assembly process. The lab first makes nanoparticles and then organizes them together to produce new properties arising from particle-particle interactions.
"In the case of our sensor, we initially found a way to organize gold nanoparticles together to form strings," Yin said. "That process is accompanied by a sharp color-change from red to blue. We speculated that the reverse—disassembly—process might have the reverse color change: from blue to red. We found to our surprise that mechanical force could achieve this disassembly. Considerable effort has been made by researchers to study nanoparticle self-assembly. Indeed, gold nanoparticles have conventionally been used as sensors based on the self-assembly process. What is novel about our work is that it shows that the disassembly process can also find great applications if the assembly is designed to be reversible."
More information: "Colorimetric Stress Memory Sensor Based on Disassembly of Gold Nanoparticle Chains" Nano Lett., Article ASAP. DOI: 10.1021/nl500144k
Abstract
We report the development of a stress-responsive colorimetric film that can memorize the stress it has experienced. The system is designed by taking advantage of the plasmonic shift associated with the disassembly of one-dimensional gold nanoparticle chains driven by the plastic deformation of the surrounding polymer matrix. By modifying the plasticity of the polymer, we demonstrate that the plasmonic shift and colorimetric change respond to a large range of stresses. This novel pressure indicating film can be used to capture and record the pressure distribution and magnitude between two contacting or impacting surfaces by outputting color information.
Journal information: Nano Letters
Provided by American Chemical Society