Electronic book for students with visual impairments reaches for the stars

A stunning Hubble Space Telescope image of the colorful 30 Doradus Nebula, a giant star-forming region, is the focal point of an eBook on stellar evolution aimed at children with visual impairments, ages 10 to 12. The book is called "Reach for the Stars: Touch, Look, Listen, Learn." Its developers have issued the first chapter, which is being previewed at the winter meeting of the American Astronomical Society at National Harbor, Md. The ebook will available in Apple's iBook store to download for free on iPads in the near future.
"Reach for the Stars" is the inspiration of astronomer Elena Sabbi of the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md., the lead researcher on the latest Hubble image of 30 Doradus, also known as the Tarantula Nebula. Sabbi and her collaborators are producing the book through a Hubble education and public outreach grant.
Although "Reach for the Stars" is being designed for children with visual impairments, Sabbi said that anyone can view and enjoy the book. "We hope it will be an inspiration and attract people to science," she explained. "That's the main goal. We want to convince children that science is cool, is fun, and that anybody could be a scientist, if they want to." Sabbi and her STScI team are developing the book in partnership with SAS, a company based in Cary, N.C., that develops analytics software to help people analyze and visualize data. The company is working to make analytics and data visualization accessible to users of all abilities, including those with visual impairments.
Ed Summers, senior manager of accessibility and applied assisted technology at SAS, is spearheading the eBook's development, leading a team of programmers, artists, and curriculum specialists. Summers, Sabbi, and Ada Lopez, a SAS science curriculum specialist, are the book's co-authors. Like Sabbi, Summers agreed that "Touch the Stars" is not solely a book for blind children. "I feel strongly that people with disabilities don't want separate materials," he said. "We want to be able to access the same materials as everybody else, but in a way that adapts to individual needs. That's why we created this mainstream book in a way that would benefit everybody, rather than something that is specifically dedicated to a relatively small audience of students with visual impairments."
The eBook will consist of six chapters and will run about 90 pages. Every page of each chapter will begin with a question, followed by a short answer. Children with a variety of learning styles will be able to see the imagery and hear the text read to them using "read aloud" technology when they touch the audio icon at the bottom of each screen. Children with visual impairments will not only hear the text read to them but also access the book using a refreshable braille display, the "VoiceOver" screen reader, or the zoom feature that is included in every iPad.
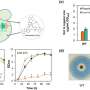
Images, graphics, videos, and animations also will appear in every chapter. Some of the images will be interactive. Several prominent star clusters in an image of the Tarantula Nebula, for example, are marked by circles. Touch a circle and a short caption appears on the screen describing the cluster.
The first chapter answers the question, why study the stars? Other chapters will include information on the history of astronomy, the different types of telescopes, what is a star, the life cycle of stars, and the Tarantula Nebula. The last chapter will provide interviews with professionals who work in astronomy, such as scientists, engineers, graphic designers, and writers.
In addition to the VoiceOver and read aloud options, the book also will offer closed captioning, a compatibility option for people with hearing aids, and a high-contrast feature for those with low vision.
SAS also is working on some special features of its own to communicate astronomy to the visually impaired. One such feature is called "sonification," which uses sound to convey graphical information. Readers will be asked to use headphones or external speakers to experience sonification's full effect. The company already has incorporated the new feature in a diagram showing the brightness of stars plotted against their surface temperature or brightnesses.
For brightness, SAS is using pitch to tell people with visual impairments the brightness of a particular star when they touch it. The brighter the star, the higher the pitch. The temperature of a star will be conveyed through either the left or right ear. Cooler stars are on the left of the graph; hotter stars are on the right. Readers will hear about a cooler star through their left ear and hotter stars through their right ear.
"It's a way to convey information that there is a trend in the distribution of stars in the diagram," Sabbi said. "If you are trying to explore the images with your finger you can get lost. This is a much stronger way to convey the information."
The book's developers also will provide tactile overlays for about 10 to 12 images in the book. The overlays will have raised textures representing important features in the image. The National Braille Press is making 200 overlays that will be available for free upon request.
SAS plans to promote the book at the American Astronomical Society and other conferences next year. The company also will market "Reach for the Stars" to teachers across the country. The Baltimore-based National Federation of the Blind, a project partner, also will help with distribution through its network of teachers and parents.
A blind college intern, Chelsea Cook, who worked for Sabbi two summers ago, was the inspiration for the book project. Sabbi was trying to figure out how Cook could work with scientific data on the computer. Max Mutchler, a scientist at STScI who has produced tactile images for people with visual impairments, suggested that Sabbi contact Ed Summers at SAS. "Ed told me that I could apply his techniques to 30 Doradus," Sabbi said. "With Chelsea, we put together a website trying to explore the nebula. That project led to the outreach grant for the book.
"'Reach for the Stars' shows the blind that there are no barriers to scare you," she added. "And technology is improving so fast that we are sure you will be able to learn and to do things. Things are becoming more reachable."
Provided by ESA/Hubble Information Centre