Building 'nanomachines' in biological outer space
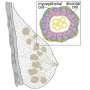
Cambridge scientists have uncovered the mechanism by which bacteria build their surface propellers (flagella) – the long extensions that allow them to swim towards food and away from danger. The results, published this week in the journal Nature, demonstrate how the mechanism is powered by the subunits themselves as they link in a chain that is pulled to the flagellum tip.
Previously, scientists thought that the building blocks for flagella were either pushed or diffused from the flagellum base through a central channel in the structure to assemble at the flagellum tip, which is located far outside the cell. However, these theories are incompatible with recent research showing that flagella grow at a constant rate. The completely new and unexpected chain mechanism, in which subunits linked in a chain 'pull themselves' through the flagellum, transforms understanding of how flagellum assembly is energised.
The research was led by Dr Gillian Fraser and Professor Colin Hughes in the University's Department of Pathology and was funded by the Wellcome Trust.
Dr Lewis Evans, who carried out the research, remarked: "It's exciting how economical bacteria are, able to harness the thermal free energy from unfolded subunits and convert it into a coherent directed transport. More broadly, it's fascinating to imagine the implications for how heat energy (normally considered as 'lost') might be harnessed to drive processes even outside living cells."
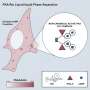
As each flagellum 'nanomachine' is assembled, thousands of subunit 'building blocks' are made in the cell and are then unfolded and exported across the cell membrane. Like other processes inside cells, this initial export phase consumes chemical energy. However, when subunits pass out of the cell into the narrow channel at the center of the growing flagellum, there is no conventional energy source and they must somehow find the energy to reach the tip.
The team has shown that at the base of the flagellum, subunits connect by head-to-tail linkage into a long chain. Together with Professor Eugene Terentjev, at the Cavendish Laboratory, they showed that the chain is pulled through the entire length of the flagellum channel by the entropic force of the unfolded subunits themselves. This produces tension in the subunit chain, which increases as each subunit refolds and incorporates into the tip of the growing structure. This pulling force automatically adjusts with increasing flagellum length, providing a constant rate of subunit delivery to the assembly site at the tip.
Professor Terentjev noted that this breakthrough can be applied to other fields. "Understanding how polymers move through channels is a fundamental physical problem. Gaining insight into this has potential applications in other disciplines, for instance in nanotechnology, specifically the building of new nanomaterials."
This research has far-reaching implications, according to Fraser. "By understanding the base-level, fundamental biology of medically important bacteria and their construction of flagella and related toxin-injecting molecular syringes," she commented, "we can start to develop new ways to counteract them."
More information: Lewis D. B. Evans, Simon Poulter, Eugene M. Terentjev, Colin Hughes & Gillian M. Fraser, "A chain mechanism for flagellum growth," Nature (2013) DOI: 10.1038/nature12682
Journal information: Nature
Provided by University of Cambridge