A cicada is pictured on a tree on July 28, 2013 in Marseille, France
Imagine a hospital room, door handle or kitchen countertop that is free from bacteria—and not one drop of disinfectant or boiling water or dose of microwaves has been needed to zap the germs.
That is the idea behind a startling discovery made by scientists in Australia.
In a study published on Tuesday in the journal Nature Communications, they described how a dragonfly led them to a nano-tech surface that physically slays bacteria.
The germ-killer is black silicon, a substance discovered accidentally in the 1990s and now viewed as a promising semiconductor material for solar panels.
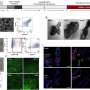
Under an electron microscope, its surface is a forest of spikes just 500 nanometres (500 billionths of a metre) high that rip open the cell walls of any bacterium which comes into contact, the scientists found.
It is the first time that any water-repellent surface has been found to have this physical quality as bactericide.
Last year, the team, led by Elena Ivanova at Swinburne University of Technology in Melbourne, were stunned to find cicada wings were potent killers of Pseudomonas aeruginsoa—an opportunist germ that also infects humans and is becoming resistant to antibiotics.
Looking closely, they found that the answer lay not in any biochemical on the wing, but in regularly-spaced "nanopillars" on which bacteria were sliced to shreds as they settled on the surface.
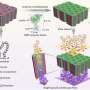
They took the discovery further by examining nanostructures studding the translucent forewings of a red-bodied Australian dragonfly called the wandering percher (Latin name Diplacodes bipunctata).
It has spikes that are somewhat smaller than those on the black silicon—they are 240 nanometres high.
Watch a video comparison of 3D models of black silicon and Diplacodes bipunctata wings.
The dragonfly's wings and black silicon were put through their paces in a lab, and both were ruthlessly bactericidal.
Smooth to the human touch, the surfaces destroyed two categories of bacteria, called Gram-negative and Gram-positive, as well as spores, the protective shell that coats certain times of dormant germs.
The three targeted bugs comprised P. aeruginosa, the notorious Staphylococcus aureus and the ultra-tough spore of Bacillus subtilis, a wide-ranging soil germ that is a cousin of anthrax.
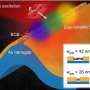
The killing rate was 450,000 bacterial cells per square centimetre per minute over the first three hours of exposure.
This is 810 times the minimum dose needed to infect a person with S. aureus, and a whopping 77,400 times that of P. aeruginosa.
If the cost of making black silicon is an obstacle, many other options are around for making nano-scale germ-killing surfaces, said the scientists.
"Synthetic antibacterial nano-materials that exhibit a similar effectiveness... can be readily fabricated over large areas," they wrote.
More information: www.nature.com/ncomms/2013/131 … full/ncomms3838.html
Journal information: Nature Communications
© 2013 AFP