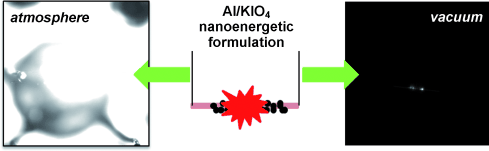
(Phys.org) —Whether they are rocket propellants or fireworks, all explosives contain a fuel and an oxidizing agent. Sometimes both are in the same molecule, like in TNT; sometimes the explosive is a mixture, like Thermite. In mixtures, the smaller the particles, the higher the explosive force. American scientists have reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie a new aerosol spray drying method for the generation of periodate nanoparticles that can be used in the formulation of highly reactive explosives.
Energetic mixtures usually have a higher energy density than explosive materials with both components in a single molecule. However, mixtures generally release the energy more slowly because the reaction partners have to find each other. Nanoenergetics researchers are attempting to achieve faster and more intensive mixing of the fuel and oxidizing agents by drastically reducing the scale of the distances involved. In most nanoenergetic formulations, nanoaluminum (aluminum nanoparticles) is used as the fuel and metal oxides as the oxidizing agents. Highly oxidizing compounds with high oxygen content, such as perchlorate are an alternative, but cannot be stored as long, partly because they are very hygroscopic. Perchlorates can also cause health problems and environmental damage. Periodates are possible substitutes. They are minimally toxic and don't absorb water. However, the production of nanoparticles of periodate salts has proven very difficult. A team led by Michael R. Zachariah at the University of Maryland has now overcome this problem. Their secret is a simple but versatile aerosol spray drying process. An aqueous solution is continuously atomized to form microdroplets, which give off water as they dry, forming nanoscopic grains of salt.
In formulations with nanoaluminum as fuel, this new nanoperiodate demonstrated superior reactivity. "Our formulations resulted in the highest gas pressure pulses described to date for nanoenergetic materials," reports Zachariah.
By using special electron microscopic and mass spectrometric techniques in which the samples can be heated extremely fast, the researchers explored the reaction mechanisms involved. They discovered that the release of gas-phase oxygen is critical for the ignition and combustion of the periodate formulations. The decomposition of potassium periodate (KIO4) takes place in two steps. First oxygen splits off. The resulting KIO3 then further decomposes to potassium iodide (KI) and oxygen. "Different from most metal oxide decompositions, the first step of periodate decomposition is exothermic, releasing heat," explains Zachariah. "This is presumably the reason for the low ignition temperature."
More information: Super-reactive Nanoenergetic Gas Generators Based on Periodate Salts, Angewandte Chemie International Edition, dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201303545
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie , Angewandte Chemie International Edition
Provided by Wiley