More emphasis needed on recycling and reuse of Li-ion batteries

The discovery of potential environmental and human health effects from disposal of millions of rechargeable lithium-ion batteries each year has led scientists to recommend stronger government policies to encourage recovery, recycling and reuse of lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery materials. That's the conclusion of a new paper in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology.
Oladele A. Ogunseitan and colleagues point out that Li-ion batteries have become mainstays for powering everything from smart phones to components in new jetliners, with global sales approaching $8 billion annually. They realized that the short life span (2-4 years) of Li-ion batteries in portable electronic devices would make a huge contribution to the electronic waste problem, which already is the fastest growing form of solid waste. So they decided to see whether potentially toxic materials leach out and become a health and environmental threat after disposal.
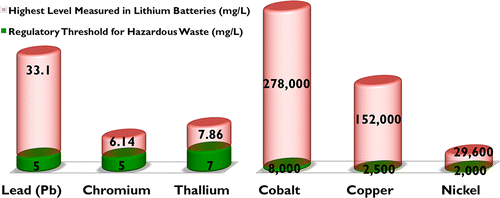
Using standardized leaching tests, hazard assessment models and other methods for evaluating hazardous waste, the scientists showed that Li-ion batteries from cell phones would meet federal government definitions of hazardous waste because of lead content. California standards would classify them as hazardous due to cobalt, copper and nickel content. "These findings support the need for stronger government policy at the local, national, and international levels to encourage recovery, recycling, and reuse of lithium battery materials," their report states.
More information: Potential Environmental and Human Health Impacts of Rechargeable Lithium Batteries in Electronic Waste, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47 (10), pp 5495–5503. DOI: 10.1021/es400614y
Abstract
Rechargeable lithium-ion (Li-ion) and lithium-polymer (Li-poly) batteries have recently become dominant in consumer electronic products because of advantages associated with energy density and product longevity. However, the small size of these batteries, the high rate of disposal of consumer products in which they are used, and the lack of uniform regulatory policy on their disposal means that lithium batteries may contribute substantially to environmental pollution and adverse human health impacts due to potentially toxic materials. In this research, we used standardized leaching tests, life-cycle impact assessment (LCIA), and hazard assessment models to evaluate hazardous waste classification, resource depletion potential, and toxicity potentials of lithium batteries used in cellphones. Our results demonstrate that according to U.S. federal regulations, defunct Li-ion batteries are classified hazardous due to their lead (Pb) content (average 6.29 mg/L; σ = 11.1; limit 5). However, according to California regulations, all lithium batteries tested are classified hazardous due to excessive levels of cobalt (average 163 544 mg/kg; σ = 62 897; limit 8000), copper (average 98 694 mg/kg; σ = 28 734; limit 2500), and nickel (average 9525 mg/kg; σ = 11 438; limit 2000). In some of the Li-ion batteries, the leached concentrations of chromium, lead, and thallium exceeded the California regulation limits. The environmental impact associated with resource depletion and human toxicity is mainly associated with cobalt, copper, nickel, thallium, and silver, whereas the ecotoxicity potential is primarily associated with cobalt, copper, nickel, thallium, and silver. However, the relative contribution of aluminum and lithium to human toxicity and ecotoxicity could not be estimated due to insufficient toxicity data in the models. These findings support the need for stronger government policy at the local, national, and international levels to encourage recovery, recycling, and reuse of lithium battery materials.
Journal information: Environmental Science & Technology
Provided by American Chemical Society