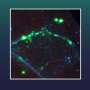
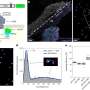
In this March 2013 photo released by the Noel Kempff Mercado Foundation, macaws perch on trunks inside a caged breeding center in the Amazon near the city of Trinidad, in the state of Beni, Bolivia. These birds are of the six endangered macaws flown from Britain to Bolivia in hopes that they can help save a species devastated by the trade in wild animals, international conservation experts said Tuesday, March 13, 2013. The birds, with blue wings and a yellow breast, arrived last week at the conservation center in northeastern Bolivia, close to their natural habitat, and the local Noel Kempff Foundation said it hopes to breed or release them. (AP Photo/Jose Diaz, Noel Kempff Mercado Foundation)
(AP)—Six endangered macaws have been flown from Britain to Bolivia in hopes that they can help save a species devastated by the trade in wild animals, international conservation experts said Tuesday.
The birds, with blue wings and a yellow breast, arrived last week at a conservation center in northeastern Bolivia, close to their natural habitat, and the local Noel Kempff Foundation said it hopes to breed or release them.
The birds were long captured for sale as pets and no more than 130 of the blue-throated macaws are believed to still exist in the wild, according to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature, which lists the birds as a critically endangered species.
"Thousands of the birds were taken from the wild in the '70s and '80s," said Alison Hales, director of the Paradise Park zoo in Hayle, a town in England's Cornwall district that bred the six birds. "There are thousands in captivity, while there are mere hundreds in the wild."
Hales, chairman of the board of the World Parrot Trust, said by telephone that conservationists have been trying for about 10 years to "maximize the breeding potential" of the few birds still remaining. But "some years there haven't been any chicks at all."
"You do your best to maximize the birds still in the world," but when that isn't working, "you think of doing something else," she said.
The director of the Bolivian foundation, Lorena Kempff, said experts there have not decided if the birds will be kept for breeding or released. "It will depend on the number of examples and characteristics of other macaws that can be repatriated," she said, referring to current efforts to bring more birds. "In any case, they are in excellent condition for both objectives."
Parrot Trust Director James D. Gilardi said by telephone that there are "only about 10 to 12 pairs of birds that attempt to breed in a good year," while in some none breed at all.
He said the conservationists working in the wild try to find as many eggs as possible and do whatever possible to protect them. That may mean propping up trees to keep them from falling or building roofs or drains to keep them from being drowned by rain.
Once they hatch, "we work with them, measure their growth rate... make sure they're developing properly" and give them food or other care if not. While that has worked, the problem is that "we're just so close to extinction that we we're doing just isn't enough."
The problem, he said, is that so few birds are spread over an area half the size of Connecticut. Once two finally meet, he said, they share a human-like issue: "You have to decide you like them and they have to like you."
The blue-throated macaw is native to the Moxos Plains, a vast savanna in the Amazon basin of northern Bolivia. The IUCN said all of its known breeding sites are on private cattle ranches, where cutting of trees has reduced the number of suitable nest sites.
Most macaws can live for 40 to 60 years in the wild.
Copyright 2013 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.