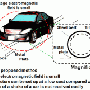
World's first demonstration of power transfer from wheels to power an electric car
Electric vehicles (EV) have ten times higher energy performance than automobiles powered by gasoline-based engines. However, they are not yet popular with drivers due to the need to store large batteries onboard. Now, Takashi Ohira and colleagues are developing an innovative method for powering EVs that drastically reduces the number of batteries.
Electric vehicles (EV) have ten times higher energy performance than automobiles powered by gasoline-based engines. EVs show tremendous potential as an effective solution to both energy shortages and global warming.
However, conventional battery-based EVs are not popular with drivers because of drawbacks including: (1) short cruising range; (2) long time to recharge; and (3) high cost. Now, assuming that these drawbacks stem from the need to store large batteries onboard cars, then there are strong demands for alternatives means of powering electric cars. In a novel approach, Takashi Ohira at Toyohashi University of Technology and colleagues are developing an innovative method for powering EVs that drastically reduces the number of batteries.
The approach exploits the steel belt usually embedded in rubber tires. The steel belt collects power excited from a pair of electrodes buried beneath the road surface. And, since the steel belt is electrically insulated by the rubber tread, the researchers used a displacement current at high frequency to penetrate from underground to the steel belt.
The researchers constructed a 1/32 scale EV to proof their concept for the electric car. The car moved successfully with a power penetration efficiency exceeding 75% at 52 MHz. This is the world-first demonstration of electric power transfer via the car-wheel to the vehicle.
"If the scheme is applied into practice, we believe it would enable a tremendous extension of the EV cruising range," says Ohira.
More information: Suzuki, Y et al., Dielectric Coupling from Electrified Roadway to Steel-Belt Tires Characterized for Miniature Model Car Running Demonstration. IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Innovative Wireless Power Transmission, IMWS-IWPT2012, pp.35-38 (2012). (DOI): 10.1109/IMWS.2012.6215814
Provided by Toyohashi University of Technology