Virtual nanoscopy: Like 'Google Earth' for cell biologists
Just as users of Google Earth can zoom in from space to a view of their own backyard, researchers can now navigate biological tissues from a whole embryo down to its subcellular structures thanks to recent advances in electron microscopy and image processing, as described in The Journal of Cell Biology (JCB). An upgrade to the JCB DataViewer (http://jcb-dataviewer.rupress.org), JCB's browser-based image presentation tool, now also makes these data publicly accessible for exploration and discovery.
Since the early days of cell biology, electron microscopy has revealed cellular structures in exquisite detail. The technique has always been limited, however, by the fact that it can only capture a tiny portion of the cell in a single image at high resolution, making it difficult for researchers to relate the structures they see to the cell as a whole, let alone to the tissue or organ in which the cell is located. Viewing samples at lower resolution, on the other hand, can reveal the larger picture of a cell or tissue, but researchers then lose the benefit of seeing fine details.
A team of scientists from Leiden University Medical Center in the Netherlands has addressed this problem by developing new tools for stitching together thousands of electron microscopy images into single, high-resolution images of biological tissues—a "Google Earth" for cell biologists—which can be explored using the newly enhanced JCB DataViewer.
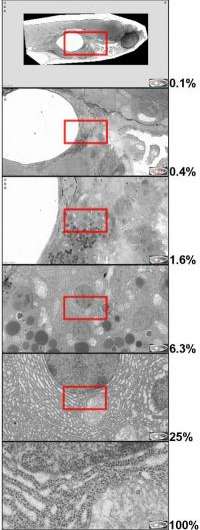
Faas et al. describe their recent advances to a technique called "virtual nanoscopy" in the August 6th issue of JCB. The researchers were able to stitch together over 26,000 individual images to generate an almost complete electron micrograph of a zebrafish embryo encompassing 281 gigapixels in total at a resolution of 16 million pixels per inch. Using the JCB DataViewer, anyone can navigate the zebrafish image from the level of the whole, 1.5 millimeter-long embryo down to subcellular structures.
The ability to integrate information across cells and tissues will provide researchers with exceptional opportunities for future discoveries. But the image's large size and complexity meant that providing access to Faas et al.'s data necessitated a major upgrade to the JCB DataViewer, a browser-based image hosting platform originally launched in 2008 to promote the sharing of original data associated with JCB publications.
"If you can image it, you should be able to publish it," says JCB Executive Editor Liz Williams. As a journal, "JCB remains committed to developing cutting-edge tools for the presentation of the data that drive progress in the field of cell biology."
More information:
Faas, F.G.A., et al. 2012. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201201140
Williams, E.H., et al. 2012. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201207117
Journal information: Journal of Cell Biology
Provided by Rockefeller University