Urinary proteomics aids early ID of diabetic nephropathy
(HealthDay) -- A biomarker classifier in urine can allow early detection of progression to diabetic nephropathy years before onset of macroalbuminuria, according to a study published online Aug. 7 in Diabetes.
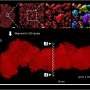
Petra Zürbig, Ph.D., from Mosaiques Diagnostics in Hannover, Germany, and colleagues profiled the low-molecular weight proteome in the urine of 35 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes using a previously generated biomarker classifier of chronic kidney disease.
The researchers found that, compared with routine diagnosis using urinary albumin, application of the classifier to normoalbuminuric patients up to five years before the onset of macroalbuminuria allowed early detection of subsequent progression to macroalbuminuria (area under the curve, 0.93 versus 0.67). In particular, there was a decrease in collagen fragments three to five years before the development of macroalbuminuria.
"Urinary proteomics enables noninvasive assessment of diabetic nephropathy risk at an early stage via determination of specific collagen fragments," Zürbig and colleagues conclude.
Several authors disclosed financial ties to pharmaceutical companies and/or Mosaiques Diagnostics, which developed and established the capillary electrophoresis coupled to mass spectrometry proteome analysis of human urine.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2012 HealthDay. All rights reserved.