The first real-world, head-to-head comparison of "improved cookstoves" (ICs) and traditional mud stoves has found that some ICs may at times emit more of the worrisome "black carbon," or soot, particles that are linked to serious health and environmental concerns than traditional mud stoves or open-cook fires. The report, which raises concerns about the leading hope as a clean cooking technology in the developing world, appears in ACS' journal Environmental Science &Technology.
Abhishek Kar, Hafeez Rehman, Jennifer Burney and colleagues explain that hundreds of millions of people in developing countries in South Asia, Africa and South America are exposed to soot from mud stoves and 3-stone fires used for cooking, heating and light. The particles can be inhaled deeply into the lungs and have been linked to health problems similar to those associated with cigarette smoking. In addition, black soot released into the atmosphere is a major factor in global warming. Aid agencies and governments have been seeking replacements for traditional cookstoves and fires to remedy those problems, with ICs as one of the leading hopes. Until now, however, there have been little real-world data on the actual performance of ICs — which have features like enhanced air flow and a battery-powered fan to burn wood and other fuel more cleanly.
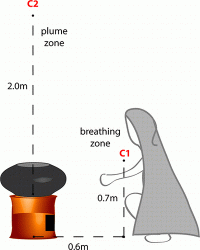
The researchers measured black carbon emissions from five IC models and traditional mud stoves. They did the test in real homes as part of Project Surya, which quantifies the impacts of cleaner cooking technologies in a village in India. Forced draft stoves burned cleaner than any other IC. However, black carbon concentrations from all ICs varied significantly, even for the same stove from one day to the next. Surprisingly, some natural draft stoves occasionally emitted more black carbon than the traditional mud cookstove.
More information: “Real-time Assessment of Black Carbon Pollution in Indian Households Due to Traditional and Improved Biomass Cookstoves” Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46 (5), pp 2993–3000. DOI: 10.1021/es203388g
Abstract
Use of improved (biomass) cookstoves (ICs) has been widely proposed as a Black Carbon (BC) mitigation measure with significant climate and health benefits. ICs encompass a range of technologies, including natural draft (ND) stoves, which feature structural modifications to enhance air flow, and forced draft (FD) stoves, which additionally employ an external fan to force air into the combustion chamber. We present here, under Project Surya, the first real-time in situ Black Carbon (BC) concentration measurements from five commercial ICs and a traditional (mud) cookstove for comparison. These experiments reveal four significant findings about the tested stoves. First, FD stoves emerge as the superior IC technology, reducing plume zone BC concentration by a factor of 4 (compared to 1.5 for ND). Indoor cooking-time BC concentrations, which varied from 50 to 1000 μg m–3 for the traditional mud cookstove, were reduced to 5–100 μg m–3 by the top-performing FD stove. Second, BC reductions from IC models in the same technology category vary significantly: for example, some ND models occasionally emit more BC than a traditional cookstove. Within the ND class, only microgasification stoves were effective in reducing BC. Third, BC concentration varies significantly for repeated cooking cycles with same stove (standard deviation up to 50% of mean concentration) even in a standardized setup, highlighting inherent uncertainties in cookstove performance. Fourth, use of mixed fuel (reflective of local practices) increases plume zone BC concentration (compared to hardwood) by a factor of 2 to 3 across ICs.
Provided by American Chemical Society