New SCUBA-2 camera reveals wild youth of the universe
.jpg)
(PhysOrg.com) -- A team of astronomers from the UK, Canada and the Netherlands have commenced a revolutionary new study of cosmic star-formation history, looking back in time to when the universe was still in its lively and somewhat unruly youth. The consortium, co-led by University of Edinburgh astrophysicist Professor James Dunlop, is using a brand new camera called SCUBA-2, the most powerful camera ever developed for observing light at "sub-mm" wavelengths (light that has a wavelength 1000 times longer than we can see with our eyes). Prof. Dunlop will present the first results from the survey on Tuesday 27 March at the National Astronomy Meeting in Manchester.
SCUBA-2 is mounted on the world's largest sub-mm telescope, the 15-metre James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT), located atop the 4,300-metre high peak of Mauna Kea in Hawaii. The new project, named the SCUBA-2 Cosmology Legacy Survey will run for 3 years and will use the camera to provide the clearest view to date of dust-enshrouded star-forming galaxies. These objects are so remote that the light we detect left them billions of years ago, so we see them as they looked in the distant past. With SCUBA-2 astronomers are able to study objects that existed as far back as 13 billion years ago, within the first billion years after the Big Bang.
Because stars form inside clouds of gas and dust, much of the ultraviolet light from young galaxies is absorbed by this cosmic dust which is then heated to a few tens of degrees above absolute zero (-273 degrees Celsius). The "warmed" (but still rather “cool”) dust then remits the absorbed energy at far-infrared wavelengths, which is then further redshifted to longer sub-mm wavelengths en-route to the Earth by the expansion of the Universe.
Detecting such emission is a challenge, both because Earth-based telescopes are warm and hence glow at sub-mm wavelengths and because water vapour in the atmosphere both absorbs and emits light in this waveband. To get around the problems of the atmosphere, the latest sub-mm surveys have recently been conducted from space, using the Herschel Space Observatory. However, the relatively small size (3.5-metre diameter) of Herschel means that the images it produces, while covering large areas, are rather fuzzy. Because its primary mirror is 20 times larger in area, the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope, now equipped with SCUBA-2, can provide a much sharper view of the sub-mm sky, especially on those occasions when the sky above the high mountain tops in Hawaii is really dry.
The SCUBA-2 Cosmology Legacy Survey is being targeted at areas on the sky which have already been studied in detail by other telescopes observing at different wavelengths. Of special importance is the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), which is undertaking a major 3-year survey (called CANDELS) of the visible light emission from high-redshift galaxies with its own new camera, Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3). By combining the JCMT and HST imaging astronomers can gain an unparalleled view of the most massive galaxies which roamed the Universe back in the "golden era" of star formation activity.
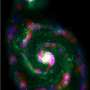
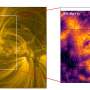
The first image presented here is made using the SCUBA-2 camera at a wavelength of 450 microns. Zooming in, it shows seven distinct sub-mm sources that appeared blended together in the poorer-quality Herschel image. The Hubble images then show that the SCUBA-2 sources are massive, clumpy, violently star-forming disc galaxies, seen at a time when the Universe was about a quarter of its present age.
Prof. Dunlop is delighted by these first deep SCUBA-2 images and looking forward to more results over the next few years. “Edinburgh scientists and engineers worked hard to construct this revolutionary new instrument and, together with our colleagues in Canada and the Netherlands, we’re now seeing the fruits of our efforts. With SCUBA-2 we can study the most violently star-forming galaxies in the young Universe, and slowly but surely start to understand how the primitive cosmos evolved into the universe we live in today.”
Provided by Royal Astronomical Society