Biologists offer clearer picture of how protein machine systems tweak gene expression
Indiana University biologists have found that specific types of RNA polymerase enzymes, the molecular machines that convert DNA into RNA, can differ in function based on variation in the parts -- in this case protein subunits -- used to assemble those machines.
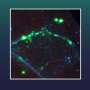
The new findings on the synthesis and function of different RNA polymerases (Pols), including two RNA polymerases that lead author Craig Pikaard discovered over a decade ago -- the plant-specific enzymes Pol IV and Pol V -- indicate that subunit composition of the polymerases plays a role in selecting how some genes are silenced while others are not.
All eukaryotes -- a group that includes plants, animals, fungi and all other organisms with nuclei -- contain life-essential Pols I, II and III that are each built from different combinations of 12 to 17 protein subunits, with each of the three enzymes assigned specific, unique tasks in the cell. In 1999 while analyzing the newly sequenced genome of Arabidopsis thaliana, a member of the mustard family considered a model organism for experimentation in plant biology, Pikaard identified Pol IV and Pol V.
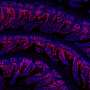
Pikaard's work has since shown that while the Pol IV and Pol V enzymes are not essential to life and are actually specialized forms of Pol II (the RNA polymerase responsible for generating RNAs that encode proteins), they play important roles in RNA-directed DNA methylation, a process that silences mobile genetic elements known as retrotransposons that can cause trouble if allowed to spread.
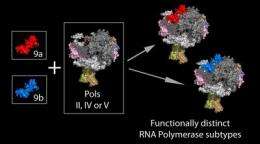
"In fact, most of the 12 protein subunits present in Pols II, IV and V are encoded by the same genes," Pikaard said. "Interestingly, among these common subunits are alternative forms of the ninth subunit, and the two forms of the ninth subunit (9a and 9b) are extremely similar, differing in only 8 of their 114 amino acids."
This high degree of similarity suggested 9a and 9b proteins might be redundant, but the Pikaard lab's new research found this to be only partially true.
"When you remove both proteins, the plants die as embryos; but if they lack just one of the proteins, they still survive, which is evidence that the two alternative forms of the protein are redundant for survival," he said. "But despite this, plants missing either 9a or 9b have different physical characteristics, such as leaf shape, suggesting that Pol II built using 9a does not function exactly the same as Pol II assembled using 9b."
Another unique feature found between the two protein subunits involves the functionality of Pol V and its ability to conduct RNA-directed DNA methylation: The Pol V polymerase built using 9b facilitates methylation, while the 9a-built Pol V does not.
"This is the first evidence showing that different functional subtypes of nuclear RNA polymerases are generated using alternative subunits, and there are multiple subunits for which more than one variant is produced," Pikaard said. "The results also show for the first time that the ninth subunit has a role in RNA-directed DNA methylation."
With new evidence from other research that RNA-directed DNA methylation and transposon silencing also takes place in the sperm-forming cell lineage in mammals, and not just in plants, Pol II transcription is implicated in methylation in both plants and animals.
"Alterations in DNA methylation and gene silencing are involved in multiple genetic disorders and diseases, including cancer," Pikaard said. "Our studies of RNA Pol IV and Pol V may tell us important things about their cousin, Pol II, that may not be possible to know otherwise, including how RNA synthesis can help specify sites of DNA methylation."
More information: "Functional consequences of subunit diversity in RNA Polymerases II and V," published March 1, 2012, in Cell Reports, authors Ek Han Tan, Todd Blevins, Thomas S. Ream and Craig S. Pikaard.
Provided by Indiana University