Advance in microchannel manufacturing opens new industry applications

Engineers at Oregon State University have invented a new way to use surface-mount adhesives in the production of low-temperature, microchannel heat exchangers - an advance that will make this promising technology much less expensive for many commercial applications.
This type of technology will be needed, researchers say, in next-generation computers, lasers, consumer electronics, automobile cooling systems, fuel processors, miniature heat pumps and more.
New industries and jobs are possible. A patent has been applied for, the findings reported in the Journal of Manufacturing Processes, and the university is seeking a partner for further commercial development.
"Even though microchannel arrays have enormous potential for more efficient heat transfer and chemical reactions, high production costs have so far held back the broad, mainstream use of the technology," said Brian Paul, a professor in the OSU School of Mechanical, Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering.
"In certain applications, this new approach has reduced material costs by 50 percent," Paul said. "It could cut production bonding costs by more than 90 percent, compared to existing approaches to microchannel lamination. And the use of surface-mount adhesives is directly translatable to the electronics assembly industry, so there is less risk going to market.
"This type of manufacturing research could enable a microchannel revolution," he said.
Microchannels, the diameter of a human hair, can be patterned into the surface of a metal or plastic, and can be designed to speed up the heat exchange between fluids, or the mixing and separation of fluids during chemical reactions. The accelerated heat and mass transfer leads to smaller heat exchangers and chemical reactors and separators, such as a portable "home dialysis" system that evolved out of previous OSU research.
Cost and production issues, however, have until now constrained the wider industrial use of this technology. The new manufacturing technique developed at OSU should help change that.
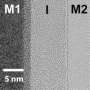
"We have demonstrated the use of surface-mount adhesives to create microchannels on a wide variety of metals, including aluminum, which is very cheap," said Prawin Paulraj, an OSU doctoral candidate and lead author on the recent study. "Bonding aluminum is difficult with conventional techniques."
These very thin pieces of patterned metal – akin to aluminum foil – can be bonded one on top of another to increase the number of microchannels in a heat exchanger, and the amount of fluid that can be processed. Creation of laminated microchannel arrays in a wide variety of materials is possible, including aluminum, copper, titanium, stainless steel and other metals.
"In computers and electronics, the heat generated by the electrical circuit is a limiting factor in how small you can make it," Paulraj said. "Microchannel process technology provides an efficient way to cool computers and consumer electronics, and make them even smaller."
The adhesives are limited in temperature to about that of boiling water. The researchers say that possible uses might include radiators to cool an automobile engine or small, very efficient heat pumps for efficient air conditioning within buildings.
More information: Metal Microchannel Lamination Using Surface Mount Adhesives for Low-Temperature Heat Exchangers, hdl.handle.net/1957/20495
Provided by Oregon State University