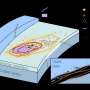
In a study published in PNAS, University of Miami scientist Rebecca Albright and colleagues report that ocean acidification could compromise the successful fertilization, larval settlement and survivorship of Elkhorn corals. The research results suggest that ocean acidification could severely impact the ability of coral reefs to recover from disturbance, said the authors. Credit: UM/RSMAS
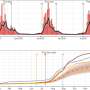
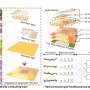
A new study led by scientists at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science suggests that over the next century recruitment of new corals could drop by 73 percent, as rising CO2 levels turn the oceans more acidic. The research findings reveal a new danger to the already threatened Caribbean and Florida reef Elkhorn corals.
"Ocean acidification is widely viewed as an emerging threat to coral reefs," said Rosenstiel School graduate student Rebecca Albright. "Our study is one of the first to document the impacts of ocean acidification on coral recruitment."
Albright and colleagues report that ocean acidification could compromise the successful fertilization, larval settlement and survivorship of Elkhorn corals. The research results suggest that ocean acidification could severely impact the ability of coral reefs to recover from disturbance, said the authors.
Elkhorn coral, known as Acropora palmata, is recognized as a critical reef-building species that once dominated tropical coral reef ecosystems. In 2006, Elkhorn was included on the U.S. Endangered Species List largely due to severe population declines over the past several decades.
Graduate student Rebecca Albright and colleagues report in the Proceedings from the National Academy of Sciences that ocean acidification could compromise the successful fertilization, larval settlement and survivorship of threatened Elkhorn corals. The research results suggest that ocean acidification could severely impact the ability of coral reefs to recover from disturbance. Credit: UM/RSMAS
The absorption of carbon dioxide by seawater, which results in a decline in pH level, is termed ocean acidification. The increased acidity in the seawater is felt throughout the marine food web as calcifying organisms, such as corals, oysters and sea urchins, find it more difficult to build their shells and skeletons making them more susceptible to predation and damage.
Recent studies, such as this one conducted by Albright and colleagues, are beginning to reveal how ocean acidification affects non-calcifying stages of marine organisms, such as reproduction.
"Reproductive failure of young coral species is an increasing concern since reefs are already highly stressed from bleaching, hurricanes, disease and poor water quality," said Chris Langdon, associate professor at the Rosenstiel School and co-author of the study.
More information: The paper, "Ocean acidification compromises recruitment success of the threatened Caribbean coral Acropora palmata," will be published in the Nov. 9 issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Provided by University of Miami