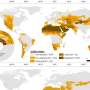
The Ballistic Missile Defense Organization's Midcourse Space Experiment satellite imaged this peak of the 1997 Leonid Meteor Shower from above 29 meteors over a 48 minute period entering the Earth's atmosphere. Image credit: BMDO/APL
(PhysOrg.com) -- The very best thing you can do to maximize your meteor shower enjoyment is get as far away from light pollution (city lights, etc.) as you can and find a location with a clear, unclouded view of the night sky that is not obstructed by trees, hills or other objects.
Once you get there, search for the darkest patch of sky you can find, as meteors can appear anywhere overhead. The path the meteors will travel will always be away from the constellation for which the shower was named. This apparent point of origin is called the "radiant." For example, meteors during a Leonid meteor shower will appear to rain in from the constellation Leo. (Note: this is an optical illusion, and the constellation only serves as a helpful guide in the night's sky. The constellation is not the actual source of the meteors.)
Now a word about the moon -- it is not your (the expectant meteor watcher's) friend. Light reflecting off a bright moon can be just as detrimental to good meteor viewing as those bright lights of the big city. There is nothing you can do except howl at the moon, so you will have to put up with it or wait until the next favorable date. Even though the 2010 Perseids and Geminids will be sharing the night sky with the moon, they are still expected to produce more visible meteor activity than other major showers without a moon.
Of the seven major meteor showers remaining in 2010 (the Quadrantids occurred in early January 2010), some are more major than others. For example, April's Lyrids are expected to produce about 15 meteors an hour at their peak for observers viewing in good conditions. Now, if you put the same observer in the same good conditions during a higher-rate shower like August's Perseids or December's Geminids, that observer could witness up to 100 meteors an hour during peak activity.
The meteor showers listed below will provide casual meteor observers with the most bang for their buck. They are easiest to observe and provide the most activity. All these showers can be best enjoyed in the hours after midnight.
2010 Meteor Showers
Lyrids
Comet of origin: C/1861 G1 Thatcher
Radiant: constellation Lyra -- which rises in the northeast at about 10 p.m.
Active: April 16-25
Peak Activity: Early Morning April 22
Peak Activity Meteor Count: Approximately 15 meteors per hour
Time of optimal viewing: On the night of expected peak activity (April 22) a moon between half and full will set between 1 and 2 a.m. for most of the northern hemisphere, leaving a dark sky until dawn. Viewers in the southern hemisphere will receive a smattering of Lyrid meteors compared to viewers north of the equator.
Meteor Velocity: Lyrid meteors hit the atmosphere at a moderate speed of 48 kilometers (30 miles) per second. They often produce luminous trains of dust that can be observed for several seconds.
Eta Aquarids
Comet of origin: 1P Halley
Radiant: constellation Aquarius
Active: April 28-May 21
Peak Activity: Early morning May 6
Peak Activity Meteor Count: Up to approximately 60 meteors per hour (southern hemisphere), 15 meteors per hour (northern hemisphere). A less-than-half-full moon is expected to severely hamper viewing
Time of optimal viewing: Just before dawn
Meteor Velocity: 67 kilometers (42 miles) per second
Delta Aquarids
Comet of origin: unknown
Radiant: constellation Aquarius
Active: July 14-Aug. 18
Peak Activity: No definite peak, but nights surrounding July 30 may be best
Peak Activity Meteor Count: Approximately 15 meteors per hour (northern hemisphere). Unfortunately, an almost-full moon will obscure many a meteor during this year's peak.
Time of optimal viewing: An hour or two before dawn. Meteor watchers in the southern hemisphere and in the northern hemisphere's tropical latitudes will enjoy the best views.
Meteor Velocity: 42 kilometers (26 miles) per second
Perseids
Comet of origin: 109P/Swift-Tuttle
Radiant: constellation Perseus
Active: Perseids begin to rise early August.
Peak Activity: Night of Aug. 12-13
Peak Activity Meteor Count: Approximately 50 meteors per hour
Time of optimal viewing: Crescent moon will set early in the evening, allowing for dark skies all the way up until peak viewing just before dawn
Meteor Velocity: 61 kilometers (38 miles) per second
Note: The Perseid meteor shower is one of the most consistent performers and considered by many as this year's best shower. The meteors they produce are among the brightest of all meteor showers.
Orionids
Comet of origin: 1P/Halley
Radiant: just to the north of constellation Orion's bright star Betelgeuse.
Active: Oct. 4-Nov. 14
Peak Activity: Night of Oct. 22, but the light reflecting off an almost-full moon makes 2010 a less-than-spectacular year for one of Mother Nature's most spectacular showers.
Peak Activity Meteor Count: Approximately 15 meteors per hour, if the sky is dark
Time of optimal viewing: An hour or two before dawn
Meteor Velocity: 68 kilometers (42 miles) per second
Note: With the second-fastest entry velocity of the annual meteor showers, meteors from the Orionids produce yellow and green colors and have been known to produce an odd fireball from time to time.
Leonids
Comet of origin: 55P/Tempel-Tuttle
Radiant: constellation Leo
Active: Nov. 7-28
Peak Activity: Night of Nov. 17-18
Peak Activity Meteor Count: Approximately 15 per hour
Time of optimal viewing: A half-full moon sets after midnight, allowing for a dark sky. Best viewing time will be just before dawn.
Meteor Velocity: 71 kilometers (44 miles) per second
Note: The Leonids have not only produced some of the best meteor showers in history, but have sometimes achieved the status of meteor storm. During a Leonid meteor storm, many thousands of meteors per hour can shoot across the sky. Scientists believe these storms recur in cycles of about 33 years, though the reason is unknown. The last documented Leonid meteor storm occurred in 2002.
Geminids
Comet of origin: 3200 Phaethon
Radiant: constellation Gemini
Active: Dec. 4-16
Peak Activity: Night of Dec 13 -14
Peak Activity Meteor Count: Approximately 50 meteors per hour
Time of optimal viewing: 2 a.m.
Meteor Velocity: 35 kilometers (22 miles) per second
Note: Generally, the Geminids or August's Perseids provide the best meteor shower show of the year. Geminids are usually considered the best opportunity for younger viewers because the show gets going around 9 or 10 p.m. Unfortunately the moon does not set until after midnight this year, making for the possibility of drooping eyelids from the pre-teen set.
Provided by JPL/NASA