Palladium Nanoparticle Electrodeposition on Nanotubes Results in New Flexible Hydrogen Sensors
In comparison to current hydrogen sensors, which are rigid and use expensive, pure palladium, Argonne's new sensors are flexible and use single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) as supports to improve efficiency and reduce cost.
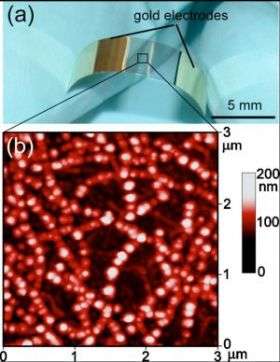
Yugang Sun and Hau Wang from ANL's Center for Nanoscale Materials fabricated the new sensing devices by using a two-step process of chemical vapor deposition and dry transfer printing. This process allows the film of nanotubes to form on the plastic, after which the palladium nanoparticles are deposited on the SWNTs to make the sensors.
According to Sun, these sensors exhibit excellent sensing performance in terms of high sensitivity, fast response time, and quick recovery, while the use of plastic sheets reduces their overall weight and increases their mechanical flexibility and shock resistance.
Flexible hydrogen sensors show a change of 75% in their resistance when exposed to hydrogen at a concentration of 0.05% in air. The devices can detect the presence of 1% hydrogen at room temperature in 3 seconds.
This work is presented in Applied Physics Letters, 90, 213107 (2007).
Source: ANL