Chrysophanol attenuates injury to hippocampal neurons in lead-exposed neonatal mice
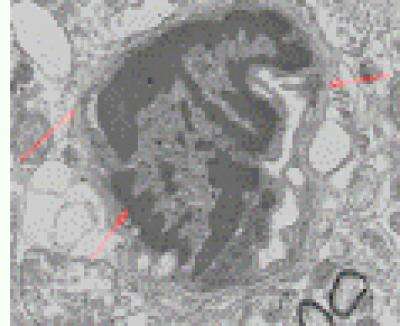
Previous studies have shown that chrysophanol protects against learning and memory impairments in lead-exposed adult mice. Ji Zhang, Hebei North University, China, proposed a hypothesis that chrysophanol can alleviate learning and memory dysfunction and hippocampal injury in lead-exposed neonatal mice.
Results showed that chrysophanol alleviated hippocampal neuronal cytoplasmic edema, promoted mitochondrial crista fusion, significantly improved learning and memory abilities, decreased lead content in blood, brain, heart, spleen, liver and kidney, increased superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities and decreased malondialdehyde level in the brain, liver and kidney of lead-exposed neonatal mice. These findings indicate that chrysophanol can significantly reduce damage to hippocampal neurons in lead-exposed neonatal mice. Related results were published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 9, 2014).
More information:
Chrysophanol attenuates lead exposure-induced injury to hippocampal neurons in neonatal mice. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(9):924-930.
Provided by Neural Regeneration Research