Chemists discover a key protein in how lysosomes work
Lysosomes, often reductively referred to as the "garbage disposals" of cells, play a pivotal role in our cells' digestive systems by getting rid of unwanted materials.

Lysosomes, often reductively referred to as the "garbage disposals" of cells, play a pivotal role in our cells' digestive systems by getting rid of unwanted materials.
Cell & Microbiology
Apr 1, 2024
0
9
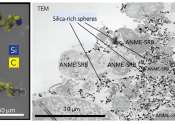
Communities of microbes that live in ocean sediments can consume methane. In oxygen-deprived sediments these microbes form clusters, called aggregates, that can have deposits of silica on their surfaces. It is not clear if ...
Cell & Microbiology
Mar 28, 2024
0
1

From pacemakers to neurostimulators, implantable medical devices rely on batteries to keep the heart on beat and to dampen pain. But batteries eventually run low and require invasive surgeries to replace.
Materials Science
Mar 27, 2024
1
164

A research team, affiliated with UNIST has achieved a groundbreaking feat by observing the dissolution of salt in water at the atomic level and experimentally uncovering the underlying principle.
Analytical Chemistry
Mar 26, 2024
0
22

In addition to their main components, the properties of crystalline and nanoporous materials often depend crucially on guest atoms or ions that are embedded in the tiny pores of their lattice structure. This applies to high-tech ...
Nanomaterials
Mar 21, 2024
0
88

Today, the word "quantum" is everywhere—in company names, movie titles, even theaters. But at its core, the concept of a quantum—the tiniest, discrete amount of something—was first developed to explain the behavior ...
Quantum Physics
Mar 19, 2024
0
123

With global goals set on transitioning away from fossil fuels, fuel cells stand out as a promising carbon-free energy source. Comprising an anode and a cathode separated by an electrolyte, fuel cells convert the chemical ...
Analytical Chemistry
Mar 14, 2024
0
17

Researchers at ETH have managed to trap ions using static electric and magnetic fields and to perform quantum operations on them. In the future, such traps could be used to realize quantum computers with far more quantum ...
Quantum Physics
Mar 13, 2024
0
50

Is there a way to stick hard and soft materials together without any tape, glue or epoxy? A new study published in ACS Central Science shows that applying a small voltage to certain objects forms chemical bonds that securely ...
Analytical Chemistry
Mar 13, 2024
1
46

When we recycle electronic devices we can no longer use, we expect to make the most out of the precious natural resources that went into building them. But electronic waste is notoriously difficult to recycle because it's ...
Biotechnology
Mar 12, 2024
0
100