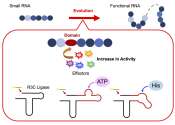
RNA's hidden potential: New study unveils its role in early life and future bioengineering
The beginning of life on Earth and its evolution over billions of years continue to intrigue researchers worldwide. The central dogma or the directional flow of genetic information from a deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) template ...