Modeling broader effects of wildfires in Siberia
As wildfires in Siberia become more common, global climate modeling estimates significant impacts on climate, air quality, health, and economies in East Asia and across the northern hemisphere.

As wildfires in Siberia become more common, global climate modeling estimates significant impacts on climate, air quality, health, and economies in East Asia and across the northern hemisphere.
Earth Sciences
16 hours ago
0
46

Even if CO2 emissions were to be drastically cut down starting today, the world economy is already committed to an income reduction of 19% until 2050 due to climate change, a study published in Nature finds. These damages ...
Economics & Business
Apr 17, 2024
0
56

New research led by the University of Oxford has found that perceptions of globally shared life experiences and globally shared biology can strengthen psychological bonding with humanity at large, which can motivate prosocial ...
Social Sciences
Apr 16, 2024
3
519

Nineteen out of 34 countries surveyed failed to fully meet their 2020 climate commitments set 15 years ago in Copenhagen, according to a new study led by UCL researchers.
Environment
Apr 16, 2024
0
91

A "rapid and far-reaching change" is necessary to prevent catastrophic climate change, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). "However, the transformation of the economy towards climate neutrality ...
Environment
Apr 15, 2024
1
86

New evidence of one of the first cities in the Pacific shows they were established much earlier than previously thought, according to new research from The Australian National University (ANU).
Archaeology
Apr 11, 2024
0
66

Cultural values may have become more different globally, but more similar regionally, over the past 40 years according to a paper published in Nature Communications. The authors suggest that over time, high-income Western ...
Social Sciences
Apr 10, 2024
0
22

Worldwide over the past 35 years, dams and land reclamation activities have converted 250,000 acres of estuary—an area roughly 17 times the size of Manhattan—to urban land or agricultural fields, with most land conversion ...
Earth Sciences
Apr 9, 2024
0
517
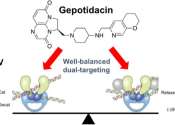
Vanderbilt biochemists are part of a team taking a stride toward the development of antibacterials to treat uncomplicated urinary tract infections, a pervasive bacterial infection that affects 50%–60% of women in their ...
Biochemistry
Mar 28, 2024
0
78

Vaccination not only reduces the severity of TB in infected cattle, but reduces its spread in dairy herds by 89%, research finds. The research, led by the University of Cambridge and Penn State University, improves prospects ...
Veterinary medicine
Mar 28, 2024
0
21
An economy consists of the economic system of a country or other area; the labor, capital and land resources; and the manufacturing, trade, distribution, and consumption of goods and services of that area. An economy may also be described as a spatially limited and social network where goods and services are exchanged according to demand and supply between participants by barter or a medium of exchange with a credit or debit value accepted within the network.
A given economy is the end result of a process that involves its technological evolution, history and social organization, as well as its geography, natural resource endowment, and ecology, as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA