Molecular discovery puts cancer treatment in a new perspective
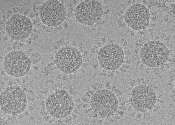
Researchers from the University of Copenhagen and the National Institutes of Health have obtained ground-breaking new knowledge about proteases - important enzymes which, among other things, play a role in the development ...