Birth gets the brain ready to sense the world

Neurons that process sensory information such as touch and vision are arranged in precise, well-characterized maps that are crucial for translating perception into understanding. A study published by Cell Press on October 14 in the journal Developmental Cell reveals that the actual act of birth in mice causes a reduction in a brain chemical called serotonin in the newborn mice, triggering sensory maps to form. The findings shed light on the key role of a dramatic environmental event in the development of neural circuits and reveal that birth itself is one of the triggers that prepares the newborn for survival outside the womb.
"Our results clearly demonstrate that birth has active roles in brain formation and maturation," says senior study author Hiroshi Kawasaki of Kanazawa University in Japan. "We found that birth regulates neuronal circuit formation not only in the somatosensory system but also in the visual system. Therefore, it seems reasonable to speculate that birth actually plays a wider role in various brain regions."
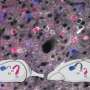
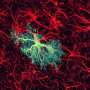
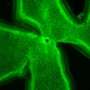
Mammals ranging from mice to humans have brain maps that represent various types of sensory information. In a region of the rodent brain known as the barrel cortex, neurons that process tactile information from whiskers are arranged in a map corresponding to the spatial pattern of whiskers on the snout, with neighboring columns of neurons responding to stimulation of adjacent whiskers. Although previous studies have shown that the neurotransmitter serotonin influences the development of sensory maps, its specific role during normal development has not been clear until now.
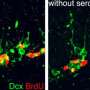
In this new study, Kawasaki and his team find that the birth of mouse pups leads to a drop in serotonin levels in the newborn's brain, triggering the formation of neural circuits in the barrel cortex and in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), a brain region that processes visual information. When mice were treated with drugs that either induced preterm birth or decreased serotonin signaling, neural circuits in the barrel cortex as well as in the LGN formed more quickly. Conversely, neural circuits in the barrel cortex failed to form when the mice were treated with a drug that increased serotonin signaling, suggesting that a reduction in levels of this neurotransmitter is crucial for sensory map formation.
Because serotonin also plays a key role in mental disorders, it is possible that abnormalities in birth processes and the effects on subsequent serotonin signaling and brain development could increase the risk of psychiatric diseases. "Uncovering the entire picture of the downstream signaling pathways of birth may lead to the development of new therapeutic methods to control the risk of psychiatric diseases induced by abnormal birth," Kawasaki says.
More information: Developmental Cell, Toda et al.: "Birth regulates the initiation of sensory map formation through serotonin signaling." dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2013.09.002