Inhibiting key enzymes kills difficult tumor cells in mice
Tumors that do not respond to chemotherapy are the target of a cancer therapy that prevents the function of two enzymes in mouse tumor cells, according to Pennsylvania medical researchers.
"We've known for well over a decade that when tumors become hypoxic they become resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy," said Wafik S. El-Deiry, M.D. Ph.D., American Cancer Society Research Professor, Rose Dunlap Professor and chief of hematology/oncology, Penn State College of Medicine. "This is a huge problem in the treatment of patients with cancer. As tumors progress, they have regions that are not well perfused with blood vessels and tumors become hypoxic."
A hypoxic tumor lacks oxygen because there are not enough blood vessels within the tumor to allow red blood cells to transport oxygen throughout the tumor.
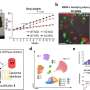
El-Deiry and his team report in a recent issue of Cancer Research that the drug sangivamycin-like molecule 3 (SLM3) helps keep tumor cells from multiplying in lab mice.
Treating a tumor with SLM3 inhibits two kinase, or enzymes: GSK-3ß, which regulates cell growth and cell death, and CDK1, which regulates cell division and blood vessel growth. Tumor cells treated with SLM3 become more sensitive to chemotherapy and die, according to El-Deiry and his colleagues.
"If you just inhibit GSK-3ß, that may not be enough and not necessarily desirable," said El-Deiry, who is also the associate director for translational research, Cancer Institute. "But there's something fortuitous about the dual targeting of these two kinases, (GSK-3ß and CDK-1), with respect to cancer therapy. If you inhibit these two kinases, the dual inhibition works together to kill hypoxic tumor cells.
"While pure inhibition of GSK-3ß can promote cell proliferation, the combination of GSK-3ß and CDK-1 inhibition not only inhibits cell proliferation but also promotes cell death," El-Deiry added.
To find SLM3, the researchers screened a chemical library looking for molecules that induce apoptosis -- cell death -- in hypoxic tumor cells. SLM3 does that, and the researchers found eight molecules whose structures were similar.
SLM3 was the version that induced the most cell death in concert with TRAIL, a naturally occurring molecule in the body that tells a cell it is time to die. TRAIL sets a process in motion that targets and shuts down tumor cells and keeps them from spreading.
SLM3, a nucleoside analog, helps keep tumor cells from multiplying by stopping cells before they duplicate their DNA. Nucleosides are the building blocks of nucleic acids and molecules like ATP -- the energy source for the body. A nucleoside analog competes with ATP and inhibits kinases, like GSK-3ß and CDK1.
GSK-3ß helps regulate cell growth and cell death. CDK1 decreases the tumor's ability to divide and generate more blood vessels. SLM3 inhibits both these kinases.
"The bottom line is the molecules actually work to shrink tumors when these molecules are combined with chemo or TRAIL therapy," El-Deiry said. "We think that these are important observations that need to be tested further in the clinic."