Researchers pursue plasmonics and photonics technology for optical improvements
Professors Mark L. Brongersma of Stanford University and Stefan A. Maier of Imperial College London are investigating new applications for terahertz sensors.
Based on their research, these sensors could be used for improving optical sources, detectors and modulators for optical interconnections and for creating biomolecules, such as plastic explosives for the Air Force.
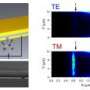
Brongersma's work is based on the unprecedented ability of nanometallic or plasmonic structures to concentrate light into deep-subwavelength volumes.
"Currently photodetectors, modulators and other chipscale devices are limited in their size by the fundamental laws of diffraction, but with plasmonics, we can make much more compact devices with one to two order of magnitude better performance parameters," said Brongersma. "As the size of these devices determines their operation speed and power, it's hard to make much more efficient devices."
Maier has demonstrated plasmon waveguides on a silicon platform operating in the telecom band, and under AFOSR support he has realized some of the first plasmonic devices operating at THz frequencies.
"The telecom band is important since that's where data communication is taking place by means of optical fibers and the Internet; the silicon platform is significant because most chips are made of that material," said Maier. "THz frequencies are vital for their sensing of dangerous substances, including plastic explosives and anthrax."
The study of plasmonics is bringing these scientists together as each works on fundamentals, information and biotechnology.
"Our team is working on demonstrating plasmon waveguides and cavities for a wide variety of applications spanning the electromagnetic spectrum from the visible to the microwave regime," said Maier.
Brongersma's group has worked on the basic concepts behind plasmonics-enabled light concentration and manipulation and is exploring a wide range of applications including faster computer chips, nanostructures synthesis, solar cells, water splitting using photoelectrochemistry, quantum optics and sensing.
Dr. Gernot Pomrenke, a program manager for the AFOSR Physics and Electronics directorate has overseen the research of these scientists for many years and Brongersma credits him with being one of the first program managers in the U.S. to realize the potential importance of plasmonics.
For their outstanding AFOSR-funded experimental and theoretical research in nano-plasmonics and nano-photonics, Brongersma and Maier were awarded the 2010 Raymond and Beverly Sackler Prize in the Physical Sciences.
"We are very excited that our fields of research have gained sufficient visibility for us to become the topics of such a prestigious prize, and we are excited and honored to share the prize equally," said Brongersma.
Provided by Air Force Office of Scientific Research