Using neutrons to peer inside a battery designed for hybrid locomotives
Rechargeable batteries may soon provide greater energy efficiency not only for road traffic, but also for rail transport. Scientists at the research neutron source FRM II of the Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM) are taking a closer look at a high performance rechargeable battery for future hybrid locomotives. The focus is on a sodium/iron chloride battery manufactured by General Electric (GE). The study reveals the distribution of chemical substances within the battery during various states of charge.
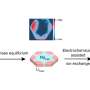
Physicists and chemists at FRM II screened a half-discharged and a fully discharged General Electric battery cell using an instrument known as ANTARES (Advanced Neutron Tomography and Radiography Experimental System). The system uses neutrons to non-destructively peer deep inside objects. The other alternative, cutting open the battery, would have allowed moisture and air to enter, thereby possibly influencing the highly reactive contents. Making use of radiography, the scientists were able to visualize the level of sodium in the unopened battery.
Using a second instrument at TUM's neutron source, the residual stress and texture diffractometer STRESS-SPEC, the scientists analyzed the exact composition of chemical substances within the cell. Each of the various materials in the battery reacts differently to the neutron radiation, thereby emitting unambiguous signals. In this way the scientists were able to determine the precise reactant distribution within the cell. This is important in establishing how the battery can be charged and discharged as often as possible.
The General Electric batteries are designed for energy savings of at least ten percent. Up to 10,000 of these 2.33 Volt batteries will provide hybrid locomotives with 2000 horsepower. Unlike the lead batteries currently used in motor vehicles, sodium/iron chloride batteries provide not only more than twice the power density, they also have very high performance, as required by locomotives. A further advantage of the batteries tested at FRM II: Unlike the lithium required for lithium batteries, sodium is readily available in nature in the form of sodium chloride, plain cooking salt.
Together with the FRM II, GE is planning to use neutrons in a real-time analysis of the charging and discharging cycles of batteries to determine with even greater precision the distribution of sodium and other substances within the batteries.
Provided by Technische Universitaet Muenchen