The Floor of Tycho Crater

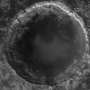
(PhysOrg.com) -- Tycho Crater is an one of the most prominent craters on the moon. It appears as a bright spot in the southern highlands with rays of bright material that stretch across much of the nearside. Its prominence is not due to its size: at 85 km in diameter, it's just one among thousands of this size or larger.
What really makes Tycho stand out is its relative youth. It formed recently enough that its beautiful rays, material ejected during the impact event, are still visible as bright streaks. All craters start out looking like this after they form, but their rays gradually fade away as they sit on the surface, exposed to the space environment which over time darkens them until they fade into the background.
How old is Tycho? Because the impact event scattered material to such great distances, it's thought that some of the samples at the Apollo 17 landing site originated at the Tycho impact site. These samples are impact melt glass, and radiometric age dating tells us that they formed 108 million years ago. So if these samples are truly from Tycho, the crater formed 108 million years ago as well. This may still seem old, but compared to the 3.9 billion-year age for many large lunar craters, Tycho is the new kid on the block. Directly sampling material from within the crater would help us learn more about not just when Tycho formed, but the ages of terrains on other planets throughout the solar system.

Planetary surfaces are dated by counting the number of craters on the surface, and comparing that number to the number of craters that formed on a surface for which we know the age by actually sampling the rocks. The problem is, there aren't that many places for which we've sampled the rocks, and confirming the age of Tycho would help date younger surfaces, which are not well sampled.
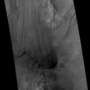
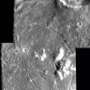
Tycho is also of great scientific interest because it is so well preserved, it is a great place to study the mechanics of how an impact crater forms. The Constellation site is on the floor of Tycho, near its central peak. The peak is thought to be material that has rebounded back up after being compressed in the impact, and though it's a peak now, it originated at greater depth than any other portion of the crater. The floor of the crater is covered in impact melt, rocks that were heated to such high temperatures during the impact event that they turned to liquid, and flowed across the floor. In the image below, impact melt flowed downhill and pooled, where it cooled.
The LROC NAC images make clear why this fascinating crater was chosen as one of the Constellation sites.
Provided by JPL/NASA