Deadly infection more common than realized
Staphylococcus aureus causes far more serious infections than previously realised, with more than 3,000 Swedes affected every year, reveals a thesis from the Sahlgrenska Academy at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden.
To date there have been no reliable data on just how common this often deadly infection is, but previously it has been estimated that just over 2,000 people are affected each year in Sweden. A population-based review of cases in the county of Skaraborg has shown that this estimate was far too low, and that the actual figure is at least 3,000 cases per annum.
"The infection can be hard to detect as it doesn't always result in a fever," says consultant Gunnar Jacobsson, who wrote the thesis. "Now that we know that it is so common, we have to be more observant with patients who have non-specific signs of infection such as a rapid pulse and difficulty breathing."
Unlike many other bacterial infections, it is not possible to vaccinate against Staphylococcus aureus. This is because the antibodies that result from vaccination are not considered to protect against new infections, though the thesis shows that the antibodies do, in fact, have a role to play.
"Those patients who had lower levels of antibodies were more likely to develop complications and die," says Jacobsson. "So it would seem that the antibodies do play some role in the body's defence system, and that a vaccine would perhaps not be without some effect."
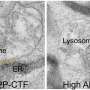
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria are often found on our skin and in our nose, where they are not dangerous. However, the bacteria can infect the body through wounds and cause septicaemia. The elderly and the infirm are most vulnerable, and anyone who is not treated with antibiotics quickly has a high risk of dying: 20 per cent of patients who contract a serious infection die within a month.