Rosetta's descent towards region of active pits

Squeezing out unique scientific observations until the very end, Rosetta's thrilling mission will culminate with a descent on 30 September towards a region of active pits on the comet's 'head'.
The region, known as Ma'at, lies on the smaller of the two lobes of Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. It is home to several active pits more than 100 m in diameter and 50–60 m in depth – where a number of the comet's dust jets originate.
The walls of the pits also exhibit intriguing metre-sized lumpy structures called 'goosebumps', which scientists believe could be the signatures of early 'cometesimals' that assembled to create the comet in the early phases of Solar System formation.
Rosetta will get its closest look yet at these fascinating structures on 30 September: the spacecraft will target a point adjacent to a 130 m-wide, well-defined pit that the mission team has informally named Deir el-Medina, after a structure with a similar appearance in an ancient Egyptian town of the same name.
Like the archaeological artefacts found inside the Egyptian pit that tell historians about life in that town, the comet's pit contains clues to the geological history of the region.
Rosetta will target a point very close to Deir el-Medina, within an ellipse about 700 × 500 m.
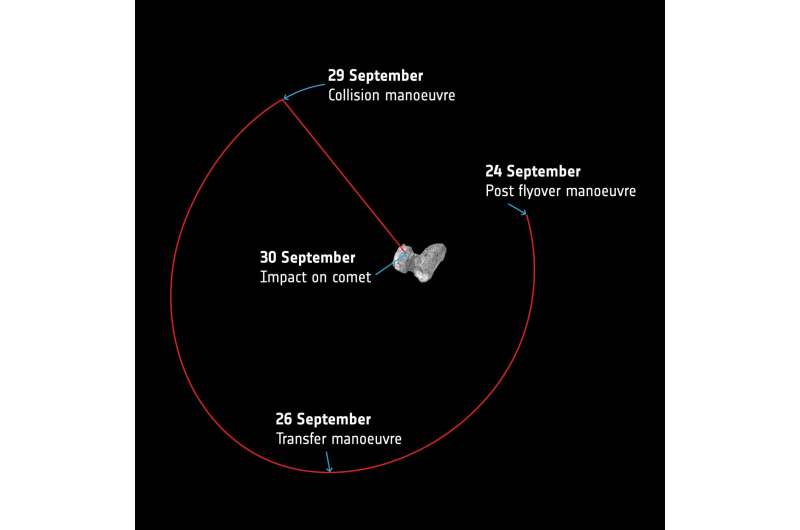
Since 9 August, Rosetta has been flying elliptical orbits that bring it progressively closer to the comet – on its closest flyby, it may come within 1 km of the surface, closer than ever before.
"Although we've been flying Rosetta around the comet for two years now, keeping it operating safely for the final weeks of the mission in the unpredictable environment of this comet and so far from the Sun and Earth, will be our biggest challenge yet," says Sylvain Lodiot, ESA's spacecraft operations manager.
"We are already feeling the difference in gravitational pull of the comet as we fly closer and closer: it is increasing the spacecraft's orbital period, which has to be corrected by small manoeuvres. But this is why we have these flyovers, stepping down in small increments to be robust against these issues when we make the final approach."
The final flyover will be complete on 24 September. Then a short series of manoeuvres needed to line Rosetta up with the target impact site will be executed over the following days as it transfers from flying elliptical orbits around the comet onto a trajectory that will eventually take it to the comet's surface on 30 September.
The collision manoeuvre will take place in the evening of 29 September, initiating the descent from an altitude of about 20 km. Rosetta will essentially free-fall slowly towards the comet in order to maximise the number of scientific measurements that can be collected and returned to Earth before its impact.
A number of Rosetta's scientific instruments will collect data during the descent, providing unique images and other data on the gas, dust and plasma very close to the comet. The exact complement of instruments and their operational timeline remains to be fixed, because it depends on constraints of the final planned trajectory and the data rate available on the day.
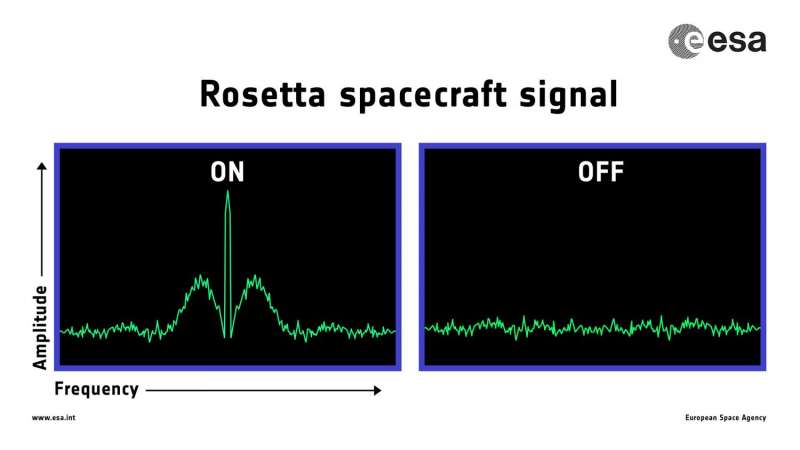
The impact is predicted to occur within 20 minutes of 10:40 UTC, with uncertainties linked to the exact trajectory of Rosetta on the day, and the influence of gravity close to the comet. Taking into account the additional 40 minute signal travel time between Rosetta and Earth on 30 September, this means that the confirmation of impact is expected at ESA's mission control in Darmstadt, Germany, within 20 minutes of 11:20 UTC (13:20 CEST). The times will be updated as the trajectory is refined.
Mirroring Rosetta's wake-up from deep space hibernation in January 2014, where a rising peak at the right frequency confirmed that the spacecraft was alive and transmitting its carrier signal, mission controllers will see that peak disappear for a final time once Rosetta impacts. It will not be possible to retrieve any data after this time.
"Last month we celebrated two thrilling years since arriving at the comet, and also a year since the comet's closest approach to the Sun along its orbit," says Matt Taylor, ESA's Rosetta project scientist.
"It's hard to believe that Rosetta's incredible 12.5 year odyssey is almost over, and we're planning the final set of science operations, but we are certainly looking forward to focusing on analysing the reams of data for many decades to come."
"This pioneering mission may be coming to an end, but it has certainly left its mark in the technical, scientific and public spheres as being one of outstanding success, with incredible achievements contributing to the current and future understanding of our Solar System," adds Patrick Martin, ESA's Rosetta mission manager.
Provided by European Space Agency