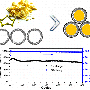Toward development of safe and durable high-temperature lithium-sulfur batteries
Safety has always been a major concern for electric vehicles, especially preventing fire and explosion incidents with the best possible battery technologies.
Lithium-sulfur batteries are considered as the most promising candidate for EVs due to their ultra-high energy density, which is over 5 times the capacity of standard commercial Li-ion batteries. This high density makes it possible for electric vehicles to travel longer distances without stopping for a charge.
However, batteries operating at the high temperatures necessary in electric vehicles presents a safety challenge, as fire and other incidents become more likely.
Prof. Andy Xueliang Sun and his University of Western Ontario research team, in collaboration with Dr. Yongfeng Hu and Dr. Qunfeng Xiao from the Canadian Light Source, have developed safe and durable high-temperature Li-S batteries using by a new coating technique called molecular layer deposition (MLD) technology for the first time. This research has been published in Nano Letters.
"Close collaboration with CLS to obtain such detailed information is very important to our understanding," said Dr. Sun. "We need not only to design novel materials for energy storage, but also deep understanding on the science behind materials."
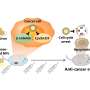
"We demonstrated that MLD alucone coating offers a safe and versatile approach toward lithium-sulfer batteries at elevated temperature," said Dr. Sun.
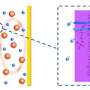
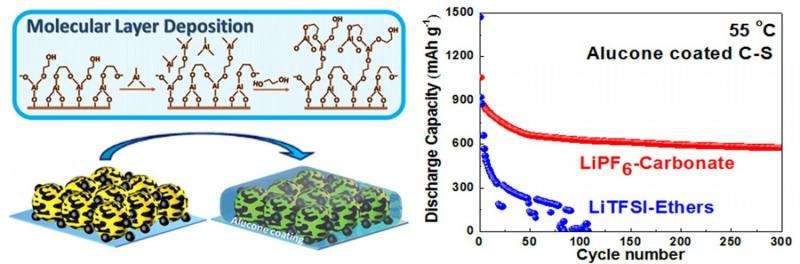
MLD is an ultrathin-film technique with applications in energy storage systems, providing precise and flexible control over film thickness and chemical composition of the target material at a molecular scale.
The MLD alucone coated carbon-sulfur electrodes demonstrated very stable and improved performance at temperatures as high as 55oC, which will significantly prolong battery life for high-temperature Li-S batteries.
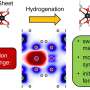
X-ray studies at the CLS revealed the specific mechanism and interaction between sulfur and alucone MLD coating.
"By using synchrotron-based high energy X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HEXPS), it demonstrated the coating ends up hindering unwanted side reactions," said Dr. Hu. This is achieved as the coating passivating the surface of the electrode.
Next up, the team will focus on the safe lithium sulfur batteries with synchrotron X-ray in-situ battery study in future.
More information: Xia Li et al. Safe and Durable High-Temperature Lithium–Sulfur Batteries via Molecular Layer Deposited Coating, Nano Letters (2016). DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00577
Journal information: Nano Letters
Provided by Canadian Light Source