Harnessing solar and wind energy in one device could power the 'Internet of Things'
The "Internet of Things" could make cities "smarter" by connecting an extensive network of tiny communications devices to make life more efficient. But all these machines will require a lot of energy. Rather than adding to the global reliance on fossil fuels to power the network, researchers say they have a new solution. Their report on a single device that harvests wind and solar energy appears in the journal ACS Nano.
Computer industry experts predict that tens of billions of gadgets will make up the Internet of Things within just five years, according to news reports. They'll be in homes, syncing coffee makers to alarm clocks. They'll be in buildings, managing lights and air temperature. But they'll also require energy to run. Sustainably generating more energy in cities close to where the devices will be used is challenging. Cities don't have much space for towering wind turbines, for example. Ya Yang, Zhong Lin Wang and colleagues wanted to find a better way to power smart cities.
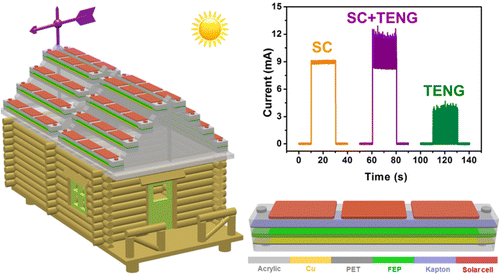
For the first time, the researchers have integrated two energy harvesting technologies in one: a silicon solar cell and a nanogenerator that can convert wind energy into electrical output. The solar cell component of the system delivers 8 milliWatts of power output (1 milliWatt can light up 100 small LEDs). The wind harvesting component delivers up to 26 milliWatts. Together, under simulated sun and wind conditions, four devices on the roof of a model home could turn on the LEDs inside and power a temperature-humidity sensor. Installed in large numbers on real rooftops, the hybrid device could help enable smart cities.
More information: Shuhua Wang et al. Efficient Scavenging of Solar and Wind Energies in a Smart City, ACS Nano (2016). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b02575
Abstract
To realize the sustainable energy supply in a smart city, it is essential to maximize energy scavenging from the city environments for achieving the self-powered functions of some intelligent devices and sensors. Although the solar energy can be well harvested by using existing technologies, the large amounts of wasted wind energy in the city cannot be effectively utilized since conventional wind turbine generators can only be installed in remote areas due to their large volumes and safety issues. Here, we rationally design a hybridized nanogenerator, including a solar cell (SC) and a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG), that can individually/simultaneously scavenge solar and wind energies, which can be extensively installed on the roofs of the city buildings. Under the same device area of about 120 mm × 22 mm, the SC can deliver a largest output power of about 8 mW, while the output power of the TENG can be up to 26 mW. Impedance matching between the SC and TENG has been achieved by using a transformer to decrease the impedance of the TENG. The hybridized nanogenerator has a larger output current and a better charging performance than that of the individual SC or TENG. This research presents a feasible approach to maximize solar and wind energies scavenging from the city environments with the aim to realize some self-powered functions in smart city.
Journal information: ACS Nano
Provided by American Chemical Society