How to cut a vortex into slices
A lot of problems associated with the mixing of the liquid in the microchannels could be solved via proper organization of the inhomogeneous slip on the walls of these channels. This is the conclusion of a joint group of Russian and German scientists lead by Olga Vinogradova, who is a professor at the M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University and also a head of laboratory at the A.N. Frumkin Institute of Physical chemistry and Electrochemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The article describing their theory was published in the latest issue of the journal Physical Review E.
This work is related to the field of microfluidics, which is a promising and rapidly developing interdisciplinary field of research involving the study fluid flow in microchannels.
Microfluidics is especially demanded in chemistry and biomedical research, where there is a necessity to carry out chemical synthesis of small doses of substance or to perform separation of particles of biomaterials.
"Microfluidics forms the basis of so-called Lab-on-a-Chip (LOC) devices, which are miniature devices that perform multistage chemical processes, including chemical reactions, mixing, concentration and separation, on a chip the size of a small coin," Olga Vinogradova says.
According to Vinogradova, such systems are promising not only as microreactors in synthetic chemistry, but also as portable analytical devices, e.g., for the diagnosis of cancer and infectious diseases. Difficulties with mixing of liquids are one of the biggest challenges in microchannels.
The flow in such channels is laminar (i.e. layered). There is no convection in laminar flow, and the liquids mix very slowly, by diffusion. Physicists managed to find a sophisticated solution to the problem based on the use of superhydrophobic surfaces. Such surfaces are made from water-repellent material. Moreover, they are microrough.
As a result, air microbubbles are retained in the recesses of a superhydrophobic surface texture. Such an "air cushion" makes superhydrophobic surfaces very slippery. In this paper, researchers have suggested using superhydrophobic textures in the form of parallel grooves, inclined at a certain angle to the axis of the channel, wherein the upper walls of the grooves are turned to the right, and at the bottom they are turned to the left. Such grooves impart the walls of the channel with anisotropic characteristics, and the liquid flows along these channels faster than it would transversely.
Moreover, apart from the main channel flow, there is a secondary shear fluid flow in the direction transverse to the axis of the channel. As a result, the fluid begins to roll slightly near the walls in the same way a bullet rotates while moving along a rifled barrel of a rifle.
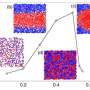
"If the fluid moves very slowly, then a very elongated transverse vortex forms in the channels," says Tatiana Nizkaya, a co-author of the paper, working at the A.N. Frumkin Institute of Physical Chemistry and Electrochemistry. "However, with an increase in liquid flow speed, the liquid begins to 'sideslip' on turns."
According to Evgeny Asmolov, who is a co-author of the paper, working at the A.N. Frumkin Institute of Physical chemistry and Electrochemistry and the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute, this vortex is superimposed by the smaller ones, which are limited by the neighboring grooves. It means that the artificial turbulence is being formed in the flow.
"Such flows may be useful for mixing liquids or for the separation of particles of different sizes," Asmolov adds.
Russian scientists, with their colleagues from the University of Mainz (Germany), carried out computer simulations of the predicted effect using dissipative particle dynamics. They analyzed the trajectory of the model of fluid particles in a microchannel and studied the dependence of the shape and the number of vortices on the flow rate.
According to the simulation results, the authors concluded that there is critical speed at which the single large vortex is broken up into many small ones, which eventually leads to a new, efficient mechanism of mixing liquids.
"Systems for efficient mixing in microchannels, based on the use of a special 'pattern' of the surface of the channel, already exist. For example, to spin liquid, specific obstacles at the bottom of the channel have a herringbone pattern. This time the vortex occurs due to the side walls," says Tatiana Nizkaya. "Our method is much easier as you simply take two superhydrophobic planes with stripes of gas and rotate them at an angle to each other.
"Furthermore, the partition of the vortex into many smaller ones allows simultaneously mixing across the width of the channel."
More information: Flows and mixing in channels with misaligned superhydrophobic walls, Physical Review E, dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.91.033020
Journal information: Physical Review E
Provided by Lomonosov Moscow State University