March 16, 2015 report
Best of Last Week—Transferring quantum states, wireless energy breakthrough and a drug that helps Alzheimer's patients
It has once again been an interesting week for physics—a team working in China demonstrated a quantum communication scheme that transferred quantum states without transmitting physical particles. They showed it was possible, using entanglement, to send quantum information between two distant points without having to send anything else. Also, a team of astrophysicists has found a possible loophole in cosmological theory that offers insight into the "lithium problem." Actual measurements used to calculate the total amount of lithium in the universe have not jibed with theory, and now a team at Université Savoie Mont Blanc is suggesting that the problem may be connected to the theory of electromagnetic cascades.
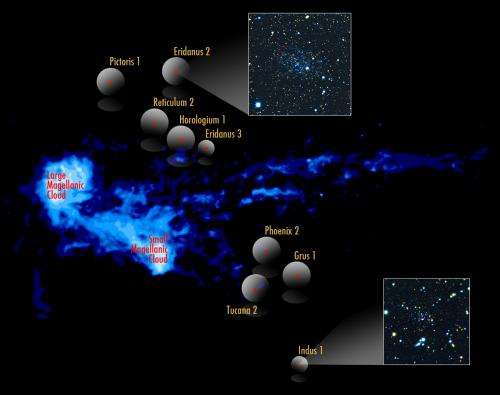
In other space news, new dwarf galaxies were discovered in orbit around the Milky Way and a team in China reported that the Yutu lunar rover found that the moon's geography is more complex than thought—its radar found at least nine distinct rock layers. And NASA explained how its revolutionary ion engine took a spacecraft to Ceres. Meanwhile, another team of researchers found evidence that suggests the Milky Way may be much larger than previously estimated—perhaps 50 percent larger.
In unrelated news, a team of researchers at Vanderbilt University has developed a network theory that sheds new light on the origins of consciousness. By studying the ways brain areas communicate with one another during the time when a person is engaged in conscious thought and applying graph theory, the team believes they have found a way to show that thinking is nothing more than widespread communication between parts of the brain. Also, a team of researchers with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency announced that they had made a wireless energy breakthrough—they found a way to use microwaves to deliver 1.8 kilowatts of power through the air to a receiver 55 meters away, potentially opening the door to a whole new way to tap solar energy.
And finally, exciting news for baby boomers and others of their generation, a team of researchers has found a drug that restores brain function and memory in early Alzheimer's disease. Thus far, it appears it might be useful for use in patients who are believed to be at high risk of developing the disease.
© 2015 Phys.org