70-foot-long, 52-ton concrete bridge survives series of simulated earthquakes (w/ Video)

A 70-foot-long, 52-ton concrete bridge survived a series of earthquakes in the first multiple-shake-table experiment in the University of Nevada, Reno's new Earthquake Engineering Lab, the newest addition to the world-renowned earthquake/seismic engineering facility.
"It was a complete success. The bridge withstood the design standard very well and today went over and above 2.2 times the design standard," John Stanton, civil and environmental engineering professor and researcher from the University of Washington, said. Stanton collaborated with Foundation Professor David Sanders of the University of Nevada, Reno in the novel experiment.
"The bridge performed very well," Sanders said. "There was a lot of movement, about 12 percent deflection – which is tremendous – and it's still standing. You could hear the rebar inside the columns shearing, like a zipper opening. Just as it would be expected to do."
The set of three columns swayed precariously, the bridge deck twisted and the sound filled the cavernous laboratory as the three 14- by 14-foot, 50-ton-capacity hydraulically driven shake tables moved the massive structure.
"Sure we broke it, but we exposed it to extreme, off-the-scale conditions," Stanton said. "The important thing is it's still standing, with the columns coming to rest right where they started, meaning it could save lives and property. I'm quite happy."

The bridge was designed and the components were pre-cast at the University of Washington in Seattle, and then built atop three 14- by 14-foot, 50-ton-capacity hydraulically driven shake tables in the 24,500 square-foot lab. It was shaken in a series of simulated earthquakes, culminating in the large ground motions similar to those recorded in the deadly and damaging 1995 magnitude 6.9 earthquake in Kobe, Japan.
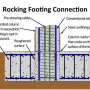
The rocking, pre-tensioned concrete bridge support system is a new bridge engineering design the team has developed with the aim of saving lives, reducing on-site construction time and minimizing earthquake damage.
"By building the components off-site we can save time with construction on-site, minimizing interruptions in traffic and lowering construction costs," Sanders said. "In this case, the concrete columns and beams were pre-cast and tensioned at the University of Washington. Other components were built here at the University of Nevada, Reno. It took us only a month to build the bridge, in what would otherwise be a lengthy process."
"This can't be done anywhere else in the nation, and perhaps the world," Ian Buckle, director of the lab and professor of civil engineering, said of the test. "Of course we've been doing these types of large-scale structures experiments for years, but it's exciting to have this first test using multiple tables in this building complete. It's good to see the equipment up and running successfully.
When combined with the University's Large-Scale Structures Laboratory, just steps away from the new lab, the facility comprises the biggest, most versatile large-scale structures, earthquake/seismic engineering facility in the United States, according to National Institute of Standards and Technology, and possibly the largest University-based facility of its kind in the world.
A grand opening was held recently for the $19 million lab expansion project, funded with $12.2 million by the U.S. Department of Commerce's National Institute of Standards and Technology, funds from the Department of Energy, as well as University and donor funds. The expansion allows a broader range of experiments and there is additional space to add a fifth large shake table.
"Our facility is unique worldwide and, combined with the excellence of our faculty and students, will allow us to make even greater contributions to the seismic safety of our state, the nation and the world," Manos Maragakis, dean of the College of Engineering, said. "We will test new designs and materials that will improve our homes, hospitals, offices and highway systems. Remarkable research is carried on here. Getting to this point has taken a lot of hard work. It's both a culmination and a beginning, ushering in a new era."
Provided by University of Nevada, Reno