Software to help plan the smart grid
(Phys.org) —Because of its vastness, complexity, and indispensability, the American power grid presents a number of different challenges to state utility commissions, legislators, energy utilities and researchers who wish to study and improve it. As part of this effort, states and the electric utility industry are working to incorporate a greater percentage of clean energy resources that power the grid – ranging from cleaner coal technologies, nuclear and natural gas to energy resources like solar, wind, waterpower, geothermal and biomass.
The power grid in the Eastern United States – known as the Eastern Interconnection – consists of transmission lines that stretch for thousands of miles, from east of the Rocky Mountains all the way to the Atlantic Seaboard. In all, 39 states and Washington, D.C. are linked by the Eastern Interconnection. To foster collaboration and better coordinate the development of this network, representatives from these states have formed an organization known as the Eastern Interconnection States' Planning Council, or EISPC.
Recently, researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory have developed a new software tool called the Energy Zones (EZ) Mapping Tool that will help EISPC members identify geographic areas suitable for the development of clean energy resources, which are renewables, natural gas, coal carbon sequestration, and nuclear. Certain forms of energy storage are also included.
"The goal of the project is to provide stakeholders with the ability to identify geographic areas with higher densities of clean energy resources, which could potentially provide a significant amount of new power generation in the future," said Argonne energy systems engineer Vladimir Koritarov. "This would also provide important information for transmission planning."
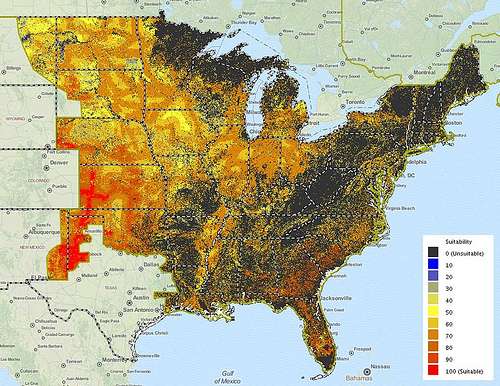
According to Koritarov, the mapping tool does not identify sites for new individual plants or clean energy "farms," but instead seeks to give a "birds-eye" view of the landscape for clean energy electricity production.
The mapping tool includes an extensive mapping library of energy resource and related information, interactive models to locate areas with high suitability for clean power generation, a variety of reports that can be run for user-specified regions, and a clean energy policy and incentives database. In all, the mapping tool database includes a total of 29 different clean energy technologies.
There are over 260 data layers in the mapping library, including energy resource, electrical transmission, pipeline, protected land, habitat, hydrology and transportation. Models in the mapping tool use maps of energy resource availability and a variety of screening factors and criteria to create "heat maps" that show the suitability of areas for clean energy resource development.
Ideally, Koritarov said, state energy planning organizations and regulators could use the mapping tool to identify suitable clean energy resource areas and potentially designate them as "clean energy zones" to promote investment by the energy industry in developing clean energy in those areas, or use the information for other state policymaking considerations.
Provided by Argonne National Laboratory