Pure gold nanoparticles can inhibit fat storage

(Phys.org) —New research reveals that pure gold nanoparticles found in everyday items such as personal care products, as well as drug delivery, MRI contrast agents and solar cells can inhibit adipose (fat) storage and lead to accelerated aging and wrinkling, slowed wound healing and the onset of diabetes. The researchers, led by Tatsiana Mironava, a visiting assistant professor in the Department of Chemical and Molecular Engineering at Stony Brook University, detail their research, "Gold nanoparticles cellular toxicity and recovery: Adipose Derived Stromal cells," in the journal Nanotoxicology.
Together with co-author Dr. Marcia Simon, Professor of Oral Biology and Pathology at Stony Brook University, and Director of the University's Living Skin Bank, a world-class facility that has developed skin tissue for burn victims and various wound therapies, the researchers tested the impact of nanoparticles in vitro on multiple types of cells, including adipose (fat) tissue, to determine whether their basic functions were disrupted when exposed to very low doses of nanoparticles. Subcutaneous adipose tissue acts as insulation from heat and cold, functions as a reserve of nutrients, and is found around internal organs for padding, in yellow bone marrow and in breast tissue.
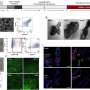
They discovered that the human adipose-derived stromal cells – a type of adult stem cells – were penetrated by the gold nanoparticles almost instantly and that the particles accumulated in the cells with no obvious pathway for elimination. The presence of the particles disrupted multiple cell functions, such as movement; replication (cell division); and collagen contraction; processes that are essential in wound healing.
According to the researchers, the most disturbing finding was that the particles interfered with genetic regulation, RNA expression and inhibited the ability to differentiate into mature adipocytes or fat cells. "Reductions caused by gold nanoparticles can result in systemic changes to the body," said Professor Mironava. "Since they have been considered inert and essentially harmless, it was assumed that pure gold nanoparticles would also be safe. Evidence to the contrary is beginning to emerge."
This study is also the first to demonstrate the impact of nanoparticles on adult stem cells, which are the cells our body uses for continual organ regeneration. It revealed that adipose derived stromal cells involved in regeneration of multiple organs, including skin, nerve, bone, and hair, ignored appropriate cues and failed to differentiate when exposed to nanoparticles. The presence of gold nanoparticles also reduced adiponectin, a protein involved in regulating glucose levels and fatty acid breakdown, which helps to regulate metabolism.
"We have learned that careful consideration and the choice of size, concentration and the duration of the clinical application of gold nanoparticles is warranted," said Professor Mironava. "The good news is that when the nanoparticles were removed, normal functions were eventually restored."
"Nanotechnology is continuing to be at the cutting edge of science research and has opened new doors in energy and materials science," said co-author, Miriam Rafailovich, PhD, Chief Scientist of the Advanced Energy Center and Distinguished Professor of Materials Science and Engineering at Stony Brook. "Progress comes with social responsibility and ensuring that new technologies are environmentally sustainable. These results are very relevant to achieving these goals."
More information: "Gold nanoparticles cellular toxicity and recovery: Adipose Derived Stromal cells," Nanotoxicology, 2013. informahealthcare.com/doi/abs/ … 17435390.2013.769128
Abstract
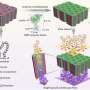
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are currently used in numerous medical applications. Herein, we describe their in vitro impact on human adipose-derived stromal cells (ADSCs) using 13 nm and 45 nm citrate-coated AuNPs. In their non-differentiated state, ADSCs were penetrated by the AuNPs and stored in vacuoles. The presence of the AuNPs in ADSCs resulted in increased population doubling times, decreased cell motility and cell-mediated collagen contraction. The degree to which the cells were impacted was a function of particle concentration, where the smaller particles required a sevenfold higher concentration to have the same effect as the larger ones. Furthermore, AuNPs reduced adipogenesis as measured by lipid droplet accumulation and adiponectin secretion. These effects correlated with transient increases in DLK1 and with relative reductions in fibronectin. Upon removal of exogenous AuNPs, cellular NP levels decreased and normal ADSC functions were restored. As adiponectin helps regulate energy metabolism, local fluctuations triggered by AuNPs can lead to systemic changes. Hence, careful choice of size, concentration and clinical application duration of AuNPs is warranted.
Journal information: Nanotoxicology
Provided by Stony Brook University