Japan whale 'research' a flashpoint in global dispute

Japan says the work that goes on at the Institute of Cetacean Research is crucial for studying whale populations; critics counter it is a way to get around an international ban on commercial whaling.
The institute can be found in a nondescript white-brick office building in Tokyo's port district.
Down a hallway and through an unmarked door is a small lobby with a model ship, a poster showing various whale species, and a sign that reads "Keep Out".
Captured whales are studied by the Institute, which refers to its work on them as "lethal research" before their meat is sold across Japan, including in restaurants in nearby Tsukiji market, where a sushi-style piece of the purple flesh costs a few dollars.
Telephone and fax requests for an interview went unanswered. An AFP reporter who visited the office recently was confronted by two men who did not identify themselves.
"What are you doing here? You are not supposed to be here. You have to leave," one said in English.
When told the taxpayer-funded institute had not responded to AFP's interview requests, he said: "That means no. It means we're not interested."
Norway and Iceland are the only other nations that hunt whales in open defiance of a 1986 moratorium, and Japan's annual hunt has drawn criticism from both activists and foreign governments.
But the Institute insists "anti-whaling is not 'world opinion'".
"Rather, it is a predominantly Western phenomenon in developed countries amplified by anti-whaling fundraising NGOs (non-governmental organisations) and the Western media," it says on its website, pointing to hundreds of whaling research papers.
"The purpose of Japan's research is science—science that will ensure that when commercial whaling is resumed it will be sustainable."
What Japan sees as research is at the heart of a bitter grudge match between militant activists intent on ending the nation's annual whale hunt and an equally determined Tokyo, which dismisses the campaigners as "terrorists".
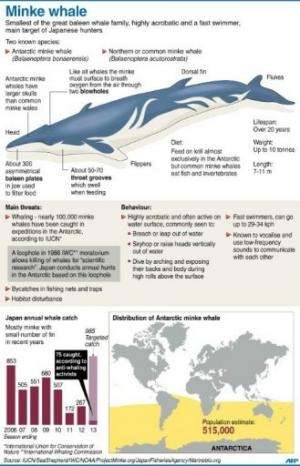
Japan's whaling fleet left port in December aiming to catch about 1,000 whales in the icy waters of the Antarctic, where they are regularly pursued by militant environmentalist group Sea Shepherd. Activists said this year's hunt ended in March with no more than 75 whales killed.
They have clashed violently in exchanges that have in the past seen stink bombs thrown at Japanese crew and water jets trained on protesters. The bitter fight has also reached the legal arena with both sides launching lawsuits.

Tokyo says that researching the mammals is "perfectly legal" under international whaling rules, as is selling meat by-products. Organs including ovaries and stomach contents are crucial for research, the Institute says.
"Some indispensable data have to be collected by lethal means, which simply cannot be obtained by non-lethal means," it says, adding that death "is as rapid as possible".
"A large proportion of the whales taken are killed instantly by an explosive harpoon".
Critics question what remains for the Institute to conclude about sustainable whale populations after carrying out its research in the decades since the moratorium on international whaling was established.
"They (the Institute) don't really have an argument to justify themselves anymore," said Junichi Sato, executive director of Greenpeace Japan.
"If they can't get enough data by killing thousands of whales, then that is a failure of the science," he said.
But "it's about pride. Japan has been claiming this is part of Japanese culture. Once you raise that issue, it's very difficult to back down."
Questions remain about the economic viability of whaling given the decades-long decline in Japanese consumption of the meat. A report by the International Fund for Animal Welfare recently said the whaling programme costs Japanese taxpayers $10 million a year.

There was little appetite among private firms to restart commercial whaling given the prohibitive expense, Sato said.
However, Fisheries minister Yoshimasa Hayashi recently told AFP in an interview that the hunt would continue, dismissing anti-whaling voices as "a cultural attack, a kind of prejudice against Japanese culture".
In the narrow streets around Tsukiji market, billed as the world's biggest fish emporium, that view was echoed by some who defended whaling as an important tradition, albeit a fading one.
Others feared job losses in the whaling sector if the hunt ended and criticised activists' in-your-face approach—even if they had little affection for whale meat itself.
"It is Japanese food culture," said 45-year-old Miuka Arita.
"People who decide they want to eat it should be allowed to do so. Just because (activists) didn't grow up eating it does not justify the aggressive actions they take," she said.
Tamie Sawai doesn't think much of "dangerous actions" by conservationists either. But the 83-year-old added that she had not eaten whale meat in years.
"Its bacon was quite good, but I don't have any strong sense of nostalgia for whale meat," she said.
"I don't miss it at all."
(c) 2013 AFP